Mot clé Void dans JavaScript
1. Le mot clé void
void est un mot clé important en ECMAScript, il comporte les caractéristiques ci-dessous :
- void agit en tant qu'opérateur, debout devant un seul opérande (single operand) avec n'importe quel type d'opérande.
- void est utilisé pour évaluer une expression. Il ne renverra aucune valeur, ou en d'autres termes, il retournera une valeur undefined (indéfinie).
L'opérateur void précède toute expression pour obtenir une valeur undefined.
void-expression-example.js
void console.log("Test1"); // Test1
console.log( void ("Test2") ); // undefined
console.log( void (2 == "2") ); // undefined
console.log( void (2) == "2" ); // false
console.log( void (2) == undefined); // true2. Void et JavaScript URIs
<a href ="javascript:URI">..</a> est commun en HTML. Les navigateurs évalueront l'URI et prendront la valeur retournée par l'URI pour remplacer le contenu de la page courante.
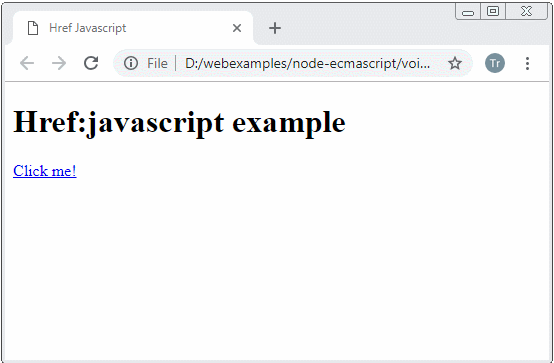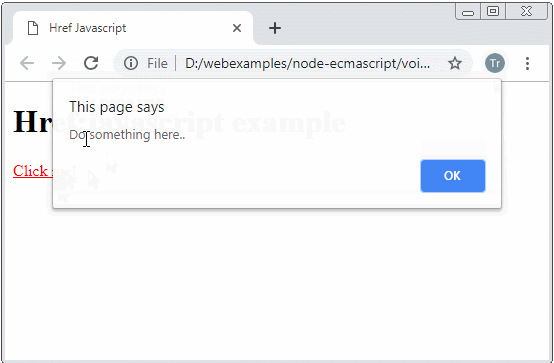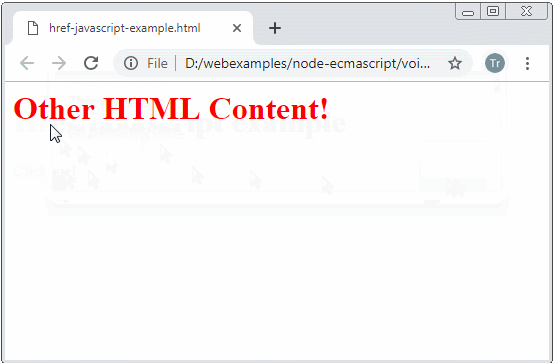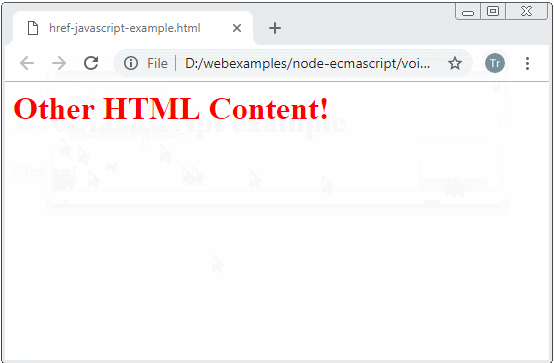
href-javascript-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Href Javascript</title>
<script>
function getHtmlContentToShow() {
console.log("Do something here...");
alert("Do something here..");
// Return new HTML content to replace current Page.
return "<h1 style='color:red;'>Other HTML Content!</h1>";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Href:javascript example</h1>
<a href="javascript:getHtmlContentToShow()">Click me!</a>
</body>
</html>Si l'URI renvoie undefined le navigateur ne va pas remplacer le contenu de la page courante
href-javascript-void-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Href Javascript Void</title>
<script>
function getHtmlContentToShow() {
console.log("Do something here...");
alert("Do something here..");
// Return new HTML content to replace current Page.
return "<h1 style='color:red;'>Other HTML Content!</h1>";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Href:javascript void example</h1>
<a href="javascript:void getHtmlContentToShow()">Click me!</a>
</body>
</html>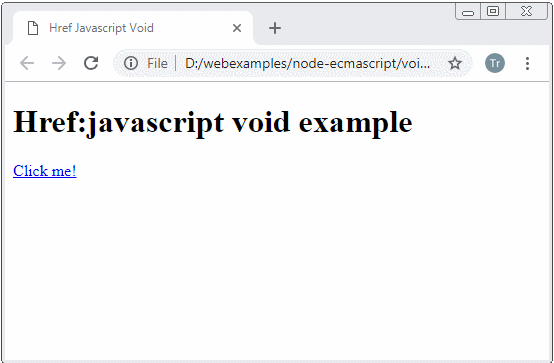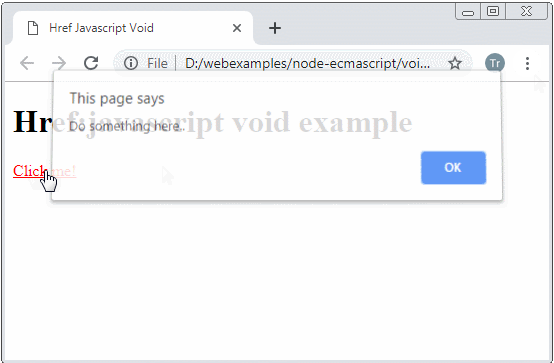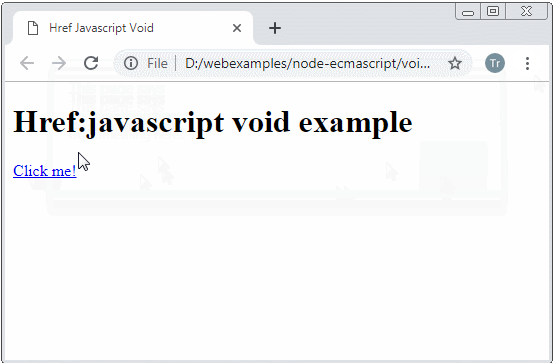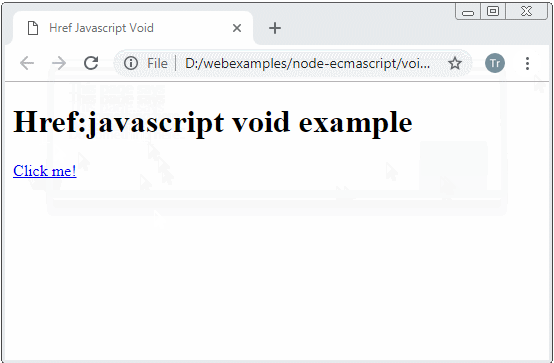
3. Fonction à sens unique
Normalement vous devriez définir une fonction et puis l'appeler.
function-example.js
// Defind a function
function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello Everyone");
}
// Call function
sayHello();L'exemple suivant vous montre comment créer une fonction à sens unique. Il est appelé immédiatement. Vous ne pourrez utiliser cette fonction nulle part ailleurs dans le programme car elle n'existe pas après avoir été utilisée.
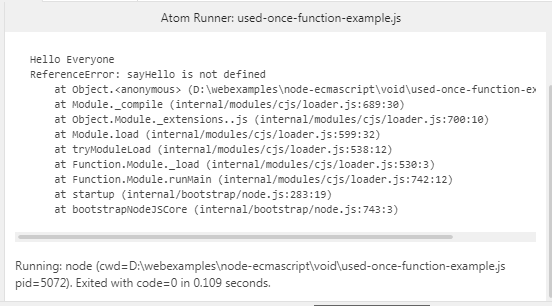
used-once-function-example.js
// Defind a function, and call it.
(function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello Everyone");
}) ();
try {
// This function does not exist.
sayHello();
}
catch(e) {
console.log(e); // ReferenceError: sayHello is not defined
}
Vous pouvez également créer une fonction à sens unique avec le mot-clé void. Il est appelé immédiatement, et n'existe plus après avoir été appelé.
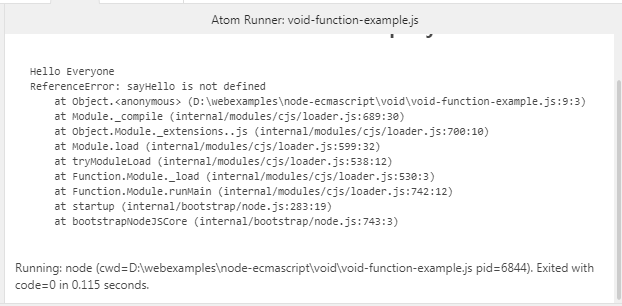
void-function-example.js
// Defind a function, and call it.
void function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello Everyone");
}();
try {
// This function does not exist.
sayHello();
}
catch(e) {
console.log(e); // ReferenceError: sayHello is not defined
}
Tutoriels de programmation ECMAScript, Javascript
- Introduction à Javascript et ECMAScript
- Démarrage rapide avec Javascript
- Boîte de dialogue Alert, Confirm, Prompt en Javascript
- Démarrage rapide avec JavaScript
- Variables dans JavaScript
- Opérations sur les bits
- Les Tableaux (Array) en JavaScript
- Boucles dans JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Function
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Number
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Boolean
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript String
- Le Tutoriel de instruction JavaScript if/else
- Le Tutoriel de instruction JavaScript switch
- Tutoriel de gestion des erreurs JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Date
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Module
- L'histoire des modules en JavaScript
- Fonctions setTimeout et setInterval dans JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Form Validation
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Web Cookie
- Mot clé Void dans JavaScript
- Classes et objets dans JavaScript
- Techniques de simulation classe et héritage en JavaScript
- Héritage et polymorphisme dans JavaScript
- Comprendre Duck Typing dans JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Symbol
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Set Collection
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Map Collection
- Comprendre JavaScript Iterable et Iterator
- Expression régulière en JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de JavaScript Promise, Async Await
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Window
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Console
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Screen
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Navigator
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Geolocation API
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Location
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript History API
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Statusbar
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Locationbar
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Scrollbars
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Menubar
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript JSON
- La gestion des événements en JavaScript
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript MouseEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript WheelEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript KeyboardEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript FocusEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript InputEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript ChangeEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript DragEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript HashChangeEvent
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript URL Encoding
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript FileReader
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript XMLHttpRequest
- Le Tutoriel de Javascript Fetch API
- Analyser XML en Javascript avec DOMParser
- Introduction à Javascript HTML5 Canvas API
- Mettre en évidence le code avec la bibliothèque Javascript de SyntaxHighlighter
- Que sont les polyfills en science de la programmation?
Show More