Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TableView
1. TableView
JavaFX fournit la class TableView qui est utilisée avec TableColumn et TableCell afin de vous aider à afficher les données sous forme de tableau (tabular form).
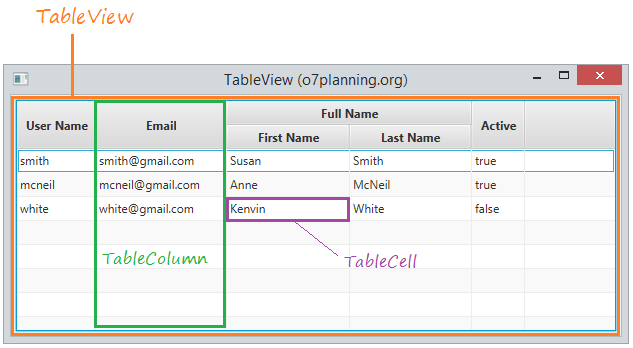
2. Ajouter une colonne au TableView
L'exemple ci-dessous crée un TableView avec les colonnes. Une colonne peut contenir des sous-colonnes.
TableViewDemo.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.tableview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.UserAccount;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TableViewDemo extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
TableView<UserAccount> table = new TableView<UserAccount>();
// Create column UserName (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> userNameCol //
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("User Name");
// Create column Email (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> emailCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Email");
// Create column FullName (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> fullNameCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Full Name");
// Create 2 sub column for FullName.
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> firstNameCol //
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("First Name");
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> lastNameCol //
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Last Name");
// Add sub columns to the FullName
fullNameCol.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol);
// Active Column
TableColumn<UserAccount, Boolean> activeCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, Boolean>("Active");
table.getColumns().addAll(userNameCol, emailCol, fullNameCol, activeCol);
StackPane root = new StackPane();
root.setPadding(new Insets(5));
root.getChildren().add(table);
stage.setTitle("TableView (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 300);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}UserAccount.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.model;
public class UserAccount {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String email;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private boolean active;
public UserAccount(Long id, String userName, String email, //
String firstName, String lastName, boolean active) {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.email = email;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.active = active;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public boolean isActive() {
return active;
}
public void setActive(boolean active) {
this.active = active;
}
}Running the example:

3. TableView avec des données
L'exemple ci-dessous illustre un TableViex avec des données. Vous pouvez mettre des colonnes qui sont triés ou non.
TableViewDemo2.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.tableview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.UserAccount;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TableViewDemo2 extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
TableView<UserAccount> table = new TableView<UserAccount>();
// Create column UserName (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> userNameCol //
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("User Name");
// Create column Email (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> emailCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Email");
// Create column FullName (Data type of String).
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> fullNameCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Full Name");
// Create 2 sub column for FullName.
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> firstNameCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("First Name");
TableColumn<UserAccount, String> lastNameCol //
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, String>("Last Name");
// Add sub columns to the FullName
fullNameCol.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol);
// Active Column
TableColumn<UserAccount, Boolean> activeCol//
= new TableColumn<UserAccount, Boolean>("Active");
// Defines how to fill data for each cell.
// Get value from property of UserAccount. .
userNameCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("userName"));
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("email"));
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("firstName"));
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("lastName"));
activeCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("active"));
// Set Sort type for userName column
userNameCol.setSortType(TableColumn.SortType.DESCENDING);
lastNameCol.setSortable(false);
// Display row data
ObservableList<UserAccount> list = getUserList();
table.setItems(list);
table.getColumns().addAll(userNameCol, emailCol, fullNameCol, activeCol);
StackPane root = new StackPane();
root.setPadding(new Insets(5));
root.getChildren().add(table);
stage.setTitle("TableView (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 300);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
private ObservableList<UserAccount> getUserList() {
UserAccount user1 = new UserAccount(1L, "smith", "smith@gmail.com", //
"Susan", "Smith", true);
UserAccount user2 = new UserAccount(2L, "mcneil", "mcneil@gmail.com", //
"Anne", "McNeil", true);
UserAccount user3 = new UserAccount(3L, "white", "white@gmail.com", //
"Kenvin", "White", false);
ObservableList<UserAccount> list = FXCollections.observableArrayList(user1, user2, user3);
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Exécutez l'exemple :

4. Modifier des données sur le Table
Vous pouvez modifier directement sur Tableview, des données seront mises à jour sur Model. L'image ci-dessous illusttre un TableView modifiable.
.
.

setCellFactory & setCellValueFactory
Vous devez fournir la manière d'afficher des données dans une cellule via la méthode tableColumn.setCellValueFactory. Et la définition d'un composant (component) (et des données de composants) seront affichées lorsque la cellule est modifiée, via la méthode tableColumn.setCellFactory.

onCellEditComit
Ensuite, vous devez définir comment des nouvelles données seront mis à jour dans le Modèle à l'aide de la méthode tableColumn.setOnEditCommit. Après la modification sur la cellule du tableau, les nouvelles données seront mises à jour dans Modèle.
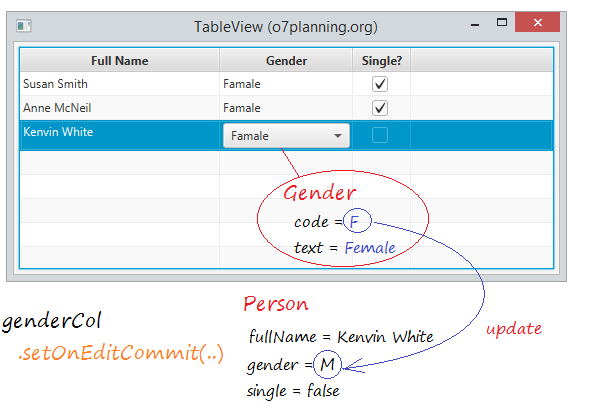
Avec les cellules montrent CheckBox sur TableView :Notez que les CheckBoxTableCell rend (render) Checkbox «en direct», ce qui signifie que le CheckBox est toujours interactive et peut être sélectionné ou désélectionné directement par l'utilisateur. Cela signifie qu'il n'est pas nécessaire que la cellule change en sont état modifiable (généralement utilisée par l'utilisateur en double-cliquant sur la cellule). Un effet secondaire de cela est que les callbacks d'édition habituelles (comme onCommitEdit) ne seront pas appelés. Si vous souhaitez être informé des modifications, vous devriez observer les propriétés booléens sont manipulés par le Checkbox.
Exemple :

TableViewEditDemo.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.tableview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.Gender;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.Person;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleBooleanProperty;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleObjectProperty;
import javafx.beans.value.ChangeListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.TableCell;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn.CellDataFeatures;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn.CellEditEvent;
import javafx.scene.control.TablePosition;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.CheckBoxTableCell;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.ComboBoxTableCell;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.TextFieldTableCell;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Callback;
public class TableViewEditDemo extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
TableView<Person> table = new TableView<Person>();
// Editable
table.setEditable(true);
TableColumn<Person, String> fullNameCol //
= new TableColumn<Person, String>("Full Name");
TableColumn<Person, Gender> genderCol//
= new TableColumn<Person, Gender>("Gender");
TableColumn<Person, Boolean> singleCol//
= new TableColumn<Person, Boolean>("Single?");
// ==== FULL NAME (TEXT FIELD) ===
fullNameCol.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<>("fullName"));
fullNameCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.<Person> forTableColumn());
fullNameCol.setMinWidth(200);
// On Cell edit commit (for FullName column)
fullNameCol.setOnEditCommit((CellEditEvent<Person, String> event) -> {
TablePosition<Person, String> pos = event.getTablePosition();
String newFullName = event.getNewValue();
int row = pos.getRow();
Person person = event.getTableView().getItems().get(row);
person.setFullName(newFullName);
});
// ==== GENDER (COMBO BOX) ===
ObservableList<Gender> genderList = FXCollections.observableArrayList(//
Gender.values());
genderCol.setCellValueFactory(new Callback<CellDataFeatures<Person, Gender>, ObservableValue<Gender>>() {
@Override
public ObservableValue<Gender> call(CellDataFeatures<Person, Gender> param) {
Person person = param.getValue();
// F,M
String genderCode = person.getGender();
Gender gender = Gender.getByCode(genderCode);
return new SimpleObjectProperty<Gender>(gender);
}
});
genderCol.setCellFactory(ComboBoxTableCell.forTableColumn(genderList));
genderCol.setOnEditCommit((CellEditEvent<Person, Gender> event) -> {
TablePosition<Person, Gender> pos = event.getTablePosition();
Gender newGender = event.getNewValue();
int row = pos.getRow();
Person person = event.getTableView().getItems().get(row);
person.setGender(newGender.getCode());
});
genderCol.setMinWidth(120);
// ==== SINGLE? (CHECH BOX) ===
singleCol.setCellValueFactory(new Callback<CellDataFeatures<Person, Boolean>, ObservableValue<Boolean>>() {
@Override
public ObservableValue<Boolean> call(CellDataFeatures<Person, Boolean> param) {
Person person = param.getValue();
SimpleBooleanProperty booleanProp = new SimpleBooleanProperty(person.isSingle());
// Note: singleCol.setOnEditCommit(): Not work for
// CheckBoxTableCell.
// When "Single?" column change.
booleanProp.addListener(new ChangeListener<Boolean>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Boolean> observable, Boolean oldValue,
Boolean newValue) {
person.setSingle(newValue);
}
});
return booleanProp;
}
});
singleCol.setCellFactory(new Callback<TableColumn<Person, Boolean>, //
TableCell<Person, Boolean>>() {
@Override
public TableCell<Person, Boolean> call(TableColumn<Person, Boolean> p) {
CheckBoxTableCell<Person, Boolean> cell = new CheckBoxTableCell<Person, Boolean>();
cell.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
return cell;
}
});
ObservableList<Person> list = getPersonList();
table.setItems(list);
table.getColumns().addAll(fullNameCol, genderCol, singleCol);
StackPane root = new StackPane();
root.setPadding(new Insets(5));
root.getChildren().add(table);
stage.setTitle("TableView (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 300);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
private ObservableList<Person> getPersonList() {
Person person1 = new Person("Susan Smith", Gender.FEMALE.getCode(), true);
Person person2 = new Person("Anne McNeil", Gender.FEMALE.getCode(), true);
Person person3 = new Person("Kenvin White", Gender.MALE.getCode(), false);
ObservableList<Person> list = FXCollections.observableArrayList(person1, person2, person3);
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Gender.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.model;
public enum Gender {
FEMALE("F", "Famale"), MALE("M", "Male");
private String code;
private String text;
private Gender(String code, String text) {
this.code = code;
this.text = text;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public static Gender getByCode(String genderCode) {
for (Gender g : Gender.values()) {
if (g.code.equals(genderCode)) {
return g;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.text;
}
}Person.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.model;
public class Person {
private String fullName;
private String gender;
private boolean single;
public Person(String fullName, String gender, boolean single) {
this.fullName = fullName;
this.gender = gender;
this.single = single;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String fullName) {
this.fullName = fullName;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public boolean isSingle() {
return single;
}
public void setSingle(boolean single) {
this.single = single;
}
}Tutoriels de JavaFX
- Ouvrir une nouvelle fenêtre (Window) dans JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ChoiceDialog
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Alert Dialog
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextInputDialog
- Installer e(fx)clipse pour Eclipse (Outillage JavaFX)
- Installer JavaFX Scene Builder pour Eclipse
- Tutoriel JavaFX pour débutant - Hello JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX FlowPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TilePane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX HBox et VBox Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX BorderPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX AnchorPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TitledPane
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Accordion
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ListView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Group
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ComboBox
- Transformations dans JavaFX
- Les effets (effects) dans JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX GridPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX StackPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ScrollPane
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX WebView et WebEngine
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX HTMLEditor
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TableView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TreeView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TreeTableView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Menu
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ContextMenu
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Image et ImageView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Label
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Hyperlink
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Button
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ToggleButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX RadioButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX MenuButton et SplitMenuButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextField
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX PasswordField
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextArea
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Slider
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Spinner
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ProgressBar et ProgressIndicator
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ChoiceBox
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Tooltip
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX DatePicker
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ColorPicker
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX FileChooser et DirectoryChooser
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX PieChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX AreaChart et StackedAreaChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX BarChart et StackedBarChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Line
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Rectangle et Ellipse
Show More