Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ListView
1. ListView
JavaFX ListView affiche ses éléments (Items) verticalement ou horizontalement.
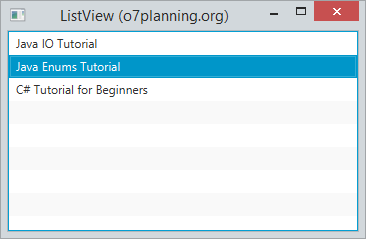
Voici une ListView vertical qui comprend 3 éléments (item).
ListView horizontal.
// Default ListView is vertical.
// Set ListView with horizontal direction.
listView.setOrientation(Orientation.HORIZONTAL);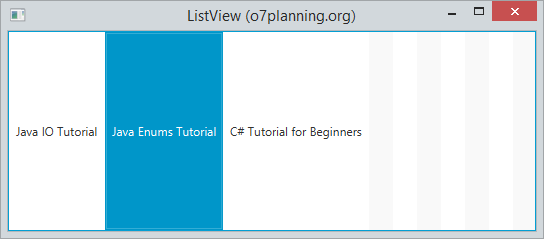
2. Exemple de ListView
ListViewDemo.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.listview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.Book;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.SelectionMode;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ListViewDemo extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Book book1 = new Book(1L, "J01", "Java IO Tutorial");
Book book2 = new Book(2L, "J02", "Java Enums Tutorial");
Book book3 = new Book(2L, "C01", "C# Tutorial for Beginners");
// To Creating a Observable List
ObservableList<Book> books = FXCollections.observableArrayList(book1, book2, book3);
// Create a ListView
ListView<Book> listView = new ListView<Book>(books);
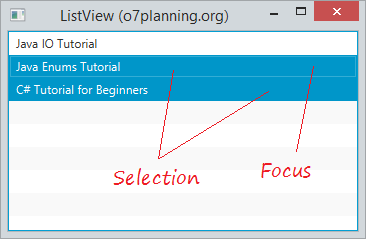
// To set multiple selection model
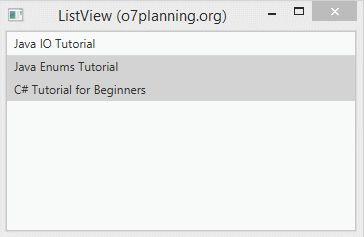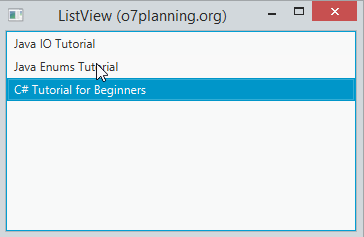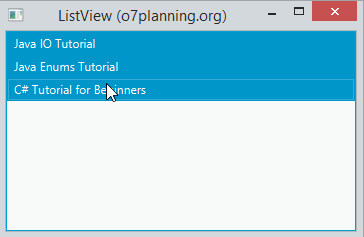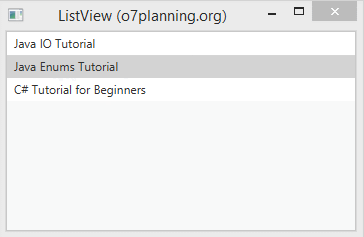
listView.getSelectionModel().setSelectionMode(SelectionMode.MULTIPLE);
// Select item at index = 1,2
listView.getSelectionModel().selectIndices(1, 2);
// Focus
listView.getFocusModel().focus(1);
StackPane root = new StackPane();
root.getChildren().add(listView);
stage.setTitle("ListView (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 350, 200);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Book.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.model;
public class Book {
private Long id;
private String code;
private String name;
public Book(Long id, String code, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}Exécutez l'exemple :
3. ListView & ChangeListener
ListViewChangeListenerExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.listview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.Book;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.value.ChangeListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.SelectionMode;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ListViewChangeListenerExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Book book1 = new Book(1L, "J01", "Java IO Tutorial");
Book book2 = new Book(2L, "J02", "Java Enums Tutorial");
Book book3 = new Book(2L, "C01", "C# Tutorial for Beginners");
Label label = new Label();
// To Creating a Observable List
ObservableList<Book> books = FXCollections.observableArrayList(book1, book2, book3);
// Create a ListView
ListView<Book> listView = new ListView<Book>(books);
// Only allowed to select single row in the ListView.
listView.getSelectionModel().setSelectionMode(SelectionMode.SINGLE);
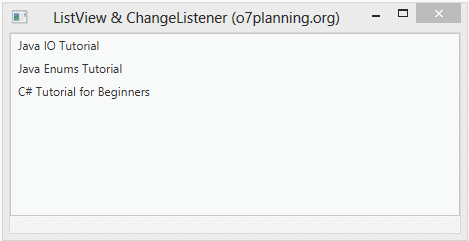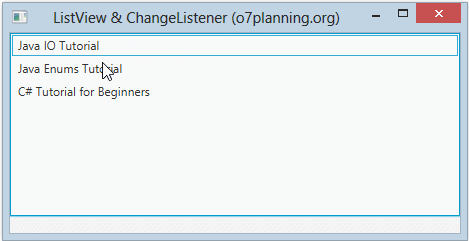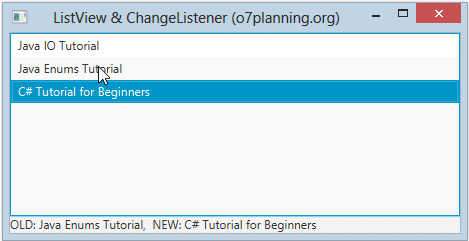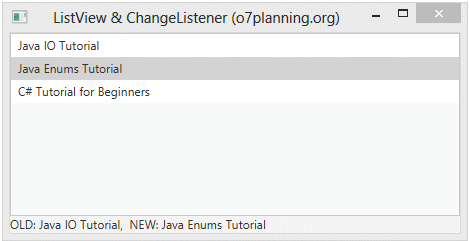
listView.getSelectionModel().selectedItemProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Book>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Book> observable, Book oldValue, Book newValue) {
label.setText("OLD: " + oldValue + ", NEW: " + newValue);
}
});
VBox root = new VBox();
root.getChildren().addAll(listView, label);
stage.setTitle("ListView & ChangeListener (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 200);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}L'événement base sur Index :
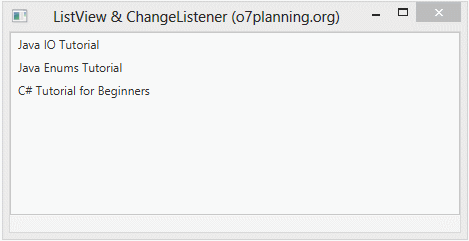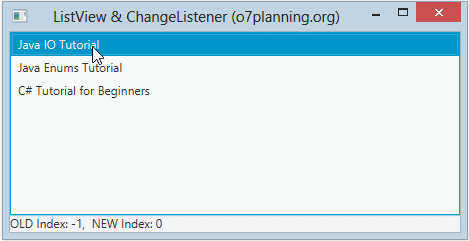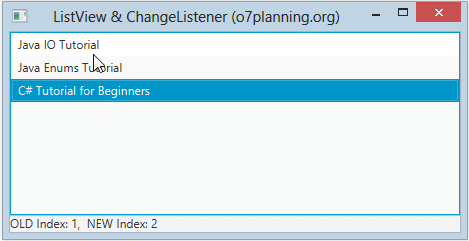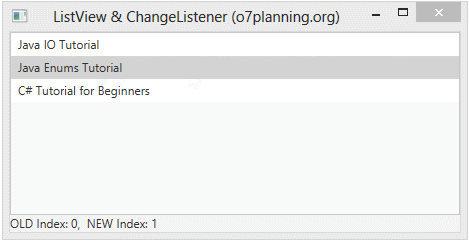
ListViewChangeListenerExample2.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.listview;
import org.o7planning.javafx.model.Book;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.value.ChangeListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.SelectionMode;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ListViewChangeListenerExample2 extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Book book1 = new Book(1L, "J01", "Java IO Tutorial");
Book book2 = new Book(2L, "J02", "Java Enums Tutorial");
Book book3 = new Book(2L, "C01", "C# Tutorial for Beginners");
Label label = new Label();
// To Creating a Observable List
ObservableList<Book> books = FXCollections.observableArrayList(book1, book2, book3);
// Create a ListView
ListView<Book> listView = new ListView<Book>(books);
// Only allowed to select single row in the ListView.
listView.getSelectionModel().setSelectionMode(SelectionMode.SINGLE);
listView.getSelectionModel().selectedIndexProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Number>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Number> observable, Number oldValue, Number newValue) {
label.setText("OLD Index: " + oldValue + ", NEW Index: " + newValue);
}
});
VBox root = new VBox();
root.getChildren().addAll(listView, label);
stage.setTitle("ListView & ChangeListener (o7planning.org)");
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 200);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}Tutoriels de JavaFX
- Ouvrir une nouvelle fenêtre (Window) dans JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ChoiceDialog
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Alert Dialog
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextInputDialog
- Installer e(fx)clipse pour Eclipse (Outillage JavaFX)
- Installer JavaFX Scene Builder pour Eclipse
- Tutoriel JavaFX pour débutant - Hello JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX FlowPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TilePane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX HBox et VBox Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX BorderPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX AnchorPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TitledPane
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Accordion
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ListView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Group
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ComboBox
- Transformations dans JavaFX
- Les effets (effects) dans JavaFX
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX GridPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX StackPane Layout
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ScrollPane
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX WebView et WebEngine
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX HTMLEditor
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TableView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TreeView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TreeTableView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Menu
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ContextMenu
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Image et ImageView
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Label
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Hyperlink
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Button
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ToggleButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX RadioButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX MenuButton et SplitMenuButton
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextField
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX PasswordField
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX TextArea
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Slider
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Spinner
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ProgressBar et ProgressIndicator
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ChoiceBox
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Tooltip
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX DatePicker
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX ColorPicker
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX FileChooser et DirectoryChooser
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX PieChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX AreaChart et StackedAreaChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX BarChart et StackedBarChart
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Line
- Le Tutoriel de JavaFX Rectangle et Ellipse
Show More