Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Scrollspy
1. Bootstrap Scrollspy
Avant de donner la définition de Scrollspy, observez un Scrollspy ci-dessous :
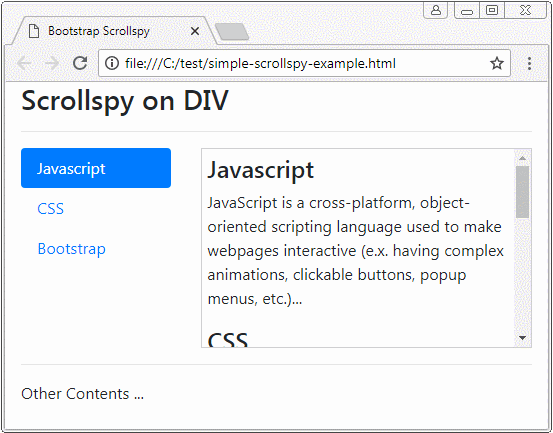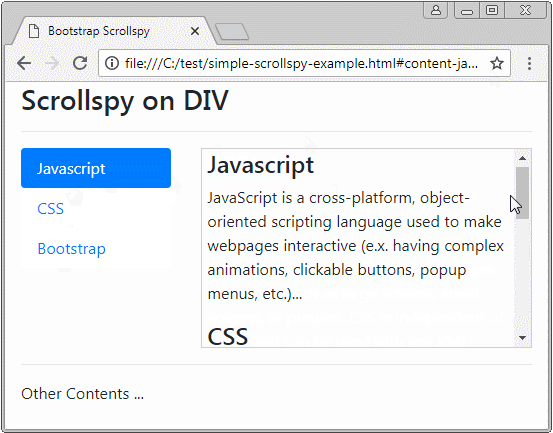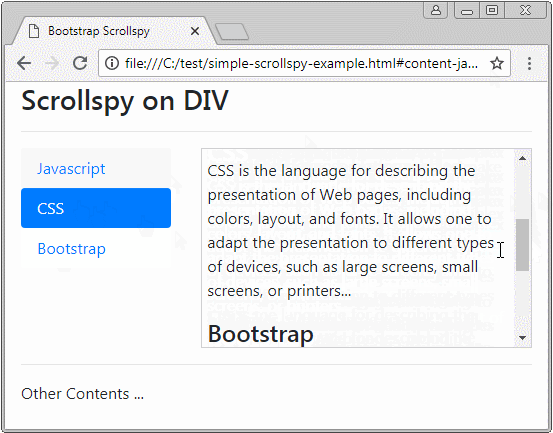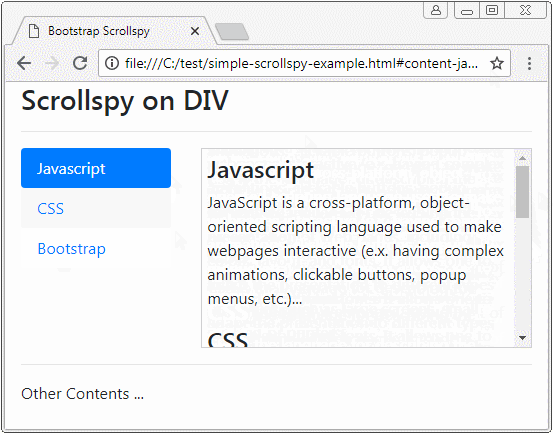
Scrollspy conformément à son nom, il signifie Scroll + Spy (Défiler + Faire de l’espionnage). Scrollspy fonctionne sur la base de 2 composants :
- Le premier composant est un Nav (ou List-Group).
- Le deuxième composant est une zone de contenu déroulable (scrollable), qui est peut être <body> ou <div>,<span>,.... Si la zone de contenu n'est pas un <body>, il est nécessaire d'établier height et overflow-y: scroll.
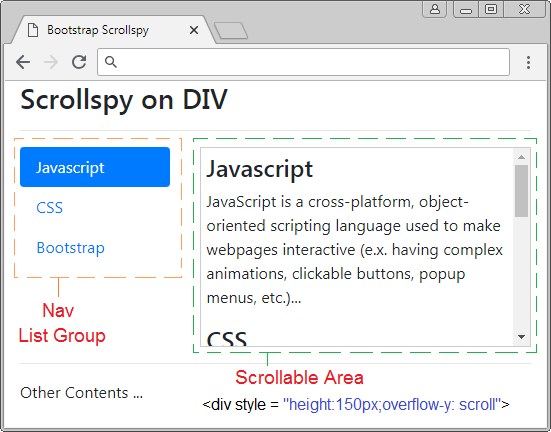
Principes de fonctionnement :
- Dans le composant 1, des utilisateurs cliquent sur un Item de Nav (ou List-Group), la barre de défilement sur le composant 2 fonctionnera pour afficher le bon contenu correspondant à Item cliqué par les utilisateurs.
- Dans le composant 2, lorsque des utilisateurs font glisser la barre de défilement, item du composant 1 correspondant au contenu affiché doit être activé (active).
simple-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy on DIV</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
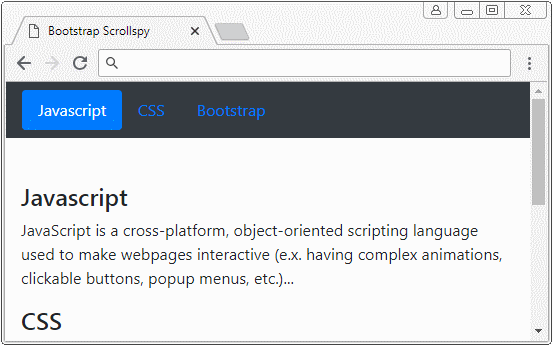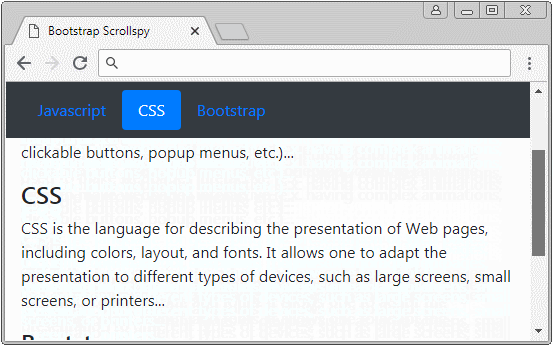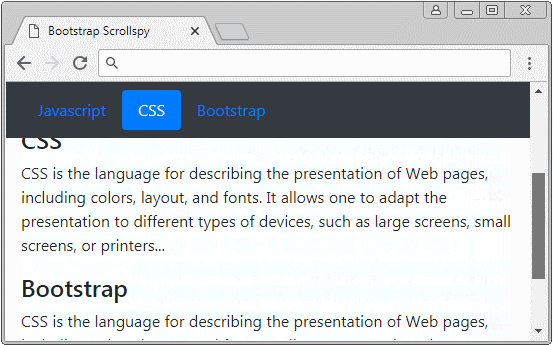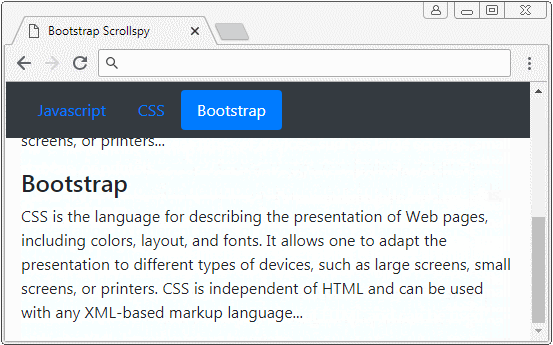
</html>2. Scrollspy + BODY
Dans cet exemple, je vais créer un Scrollspy pour "espionner" (spy) le contenu de <body>. Il est à noter que le <body> par défaut a une barre de défilement verticale (vertical scrollbar), qui est la barre de défilement du navigateur. Voici l'illustration de la structure de cet exemple :
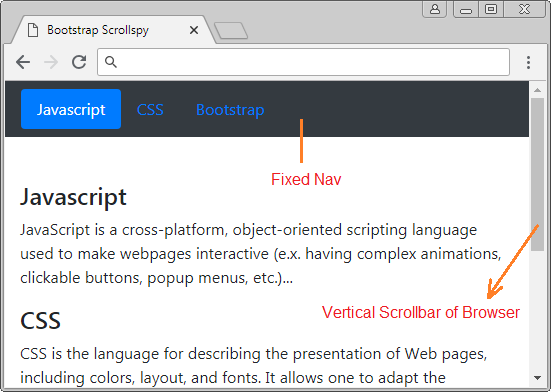
body-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body data-spy="scroll" data-target="#scrollspy-nav" data-offset="110">
<div class="container-fluid">
<nav id="scrollspy-nav" class="navbar bg-dark fixed-top">
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div style="margin-top:100px;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
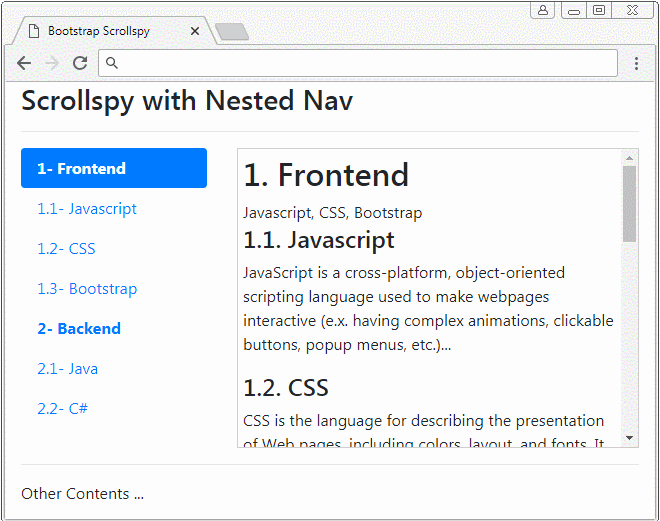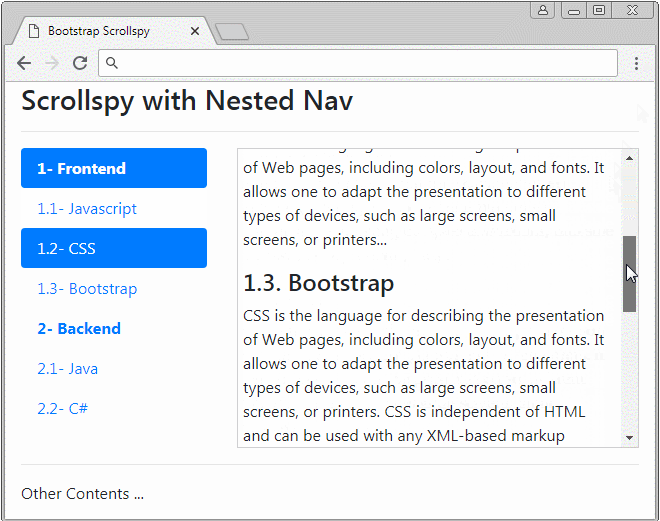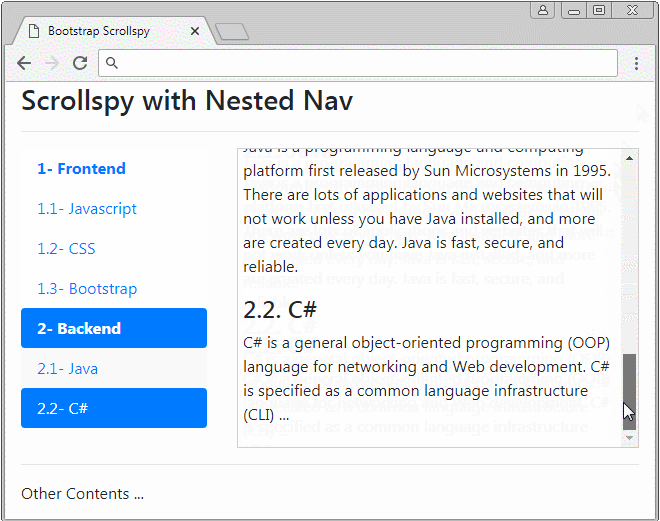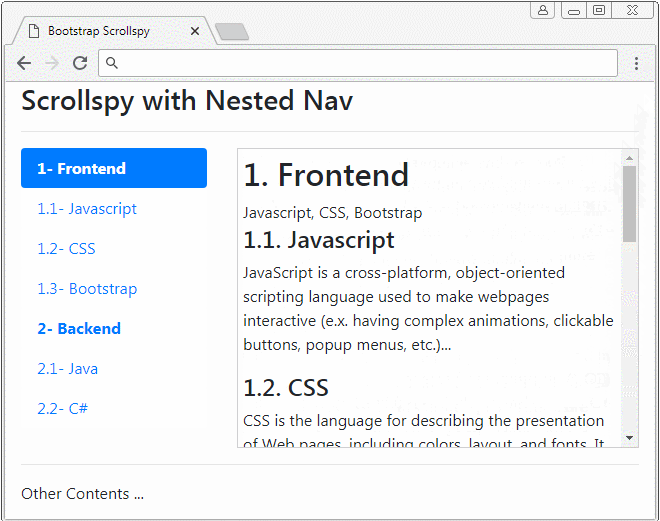
</html>3. Exemple de Nav niché (Nested Nav)
Scrollspy travaille également avec Nav niché (Nested Navs). Si un Nav est activé (active) Nav parent est également activé.
nested-nav-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with Nested Navs</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-frontend">
<strong>1- Frontend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript"> 1.1- Javascript</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-css"> 1.2- CSS</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap"> 1.3- Bootstrap</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-backend">
<strong>2- Backend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-java"> 2.1- Java</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-csharp"> 2.2- C#</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:300px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h2 id="content-frontend">1. Frontend</h2>
Javascript, CSS, Bootstrap
<h4 id="content-javascript">1.1. Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language
used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">1.2. CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">1.3. Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
<h2 id="content-backend">2. Backend</h2>
Java, C#
<h4 id="content-java">2.1. Java</h4>
<p>
Java is a programming language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995.
There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed,
and more are created every day. Java is fast, secure, and reliable.
</p>
<h4 id="content-csharp">2.2. C#</h4>
<p>
C# is a general object-oriented programming (OOP) language for networking and Web development.
C# is specified as a common language infrastructure (CLI) ...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>4. Exemple de List Group
Scrollspy travaille également avec List Group. Ci-dessous un exemple :
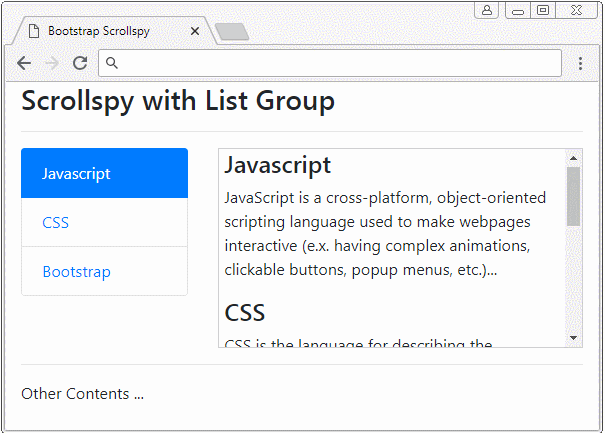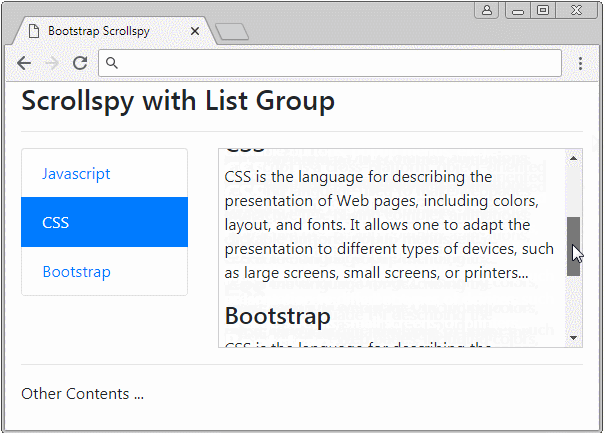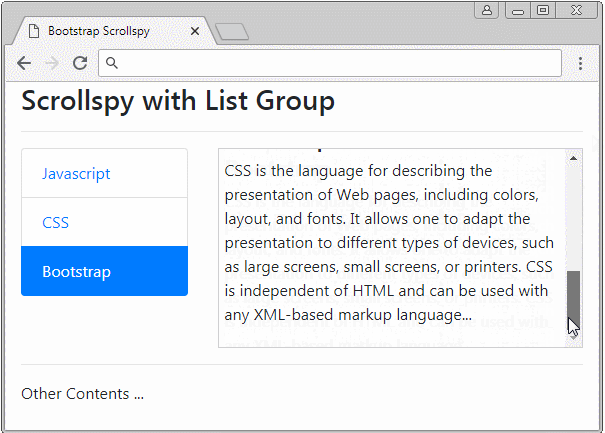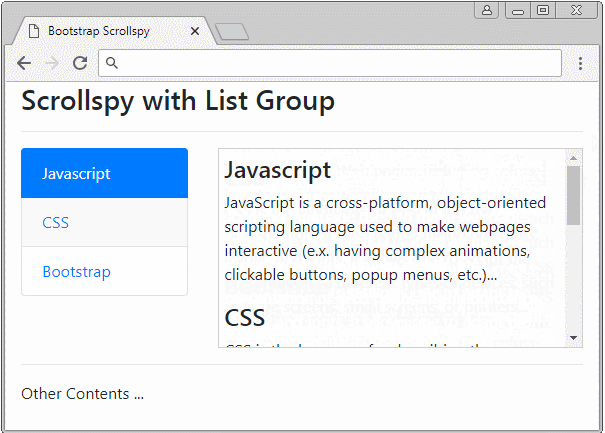
list-group-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with List Group</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<div class="list-group" id="myScrollspy">
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-css">CSS</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Tutoriels de programmation Bootstrap
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Jumbotron
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Dropdown
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Alert
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Button
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Button Group
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Popover (Tooltip)
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Spinner
- Introduction à Bootstrap
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Grid System
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Card
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Container
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Nav, Tab, Pill
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap NavBar
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Table
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Modal
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Form
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Pagination
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Badge
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Input Group
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap List Group
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap ProgressBar
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Collapse et Accordion
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Scrollspy
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Breadcrumb
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Carousel
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Spacing Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Border Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Color Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Text Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Sizing Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Position Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Flex Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Display Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Visibility Utility
- Le Tutoriel de Bootstrap Embed Utility
Show More