Invocation de méthode à distance en Java
1. Introduction
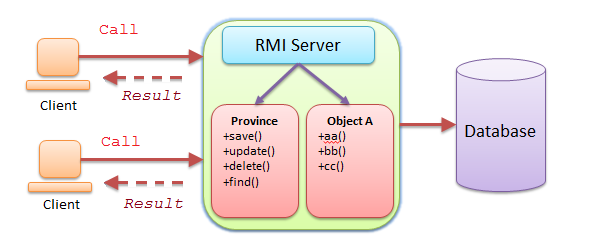
RMI est un moyen pour vous d'appeler une méthode à distance. Par exemple, appeler une méthode exécutée sur un ordinateur B et recevoir la réponse finale. L'ordinateur B est ainsi un service de fourniture de serveur.
2. Créer un projet
Créer un nouveau projet baptisé RMITutorial
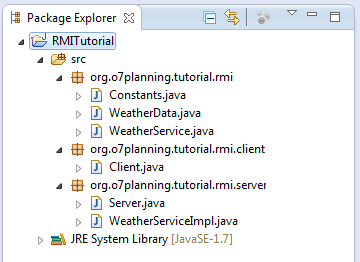
Les classes emballées pour Client et Server
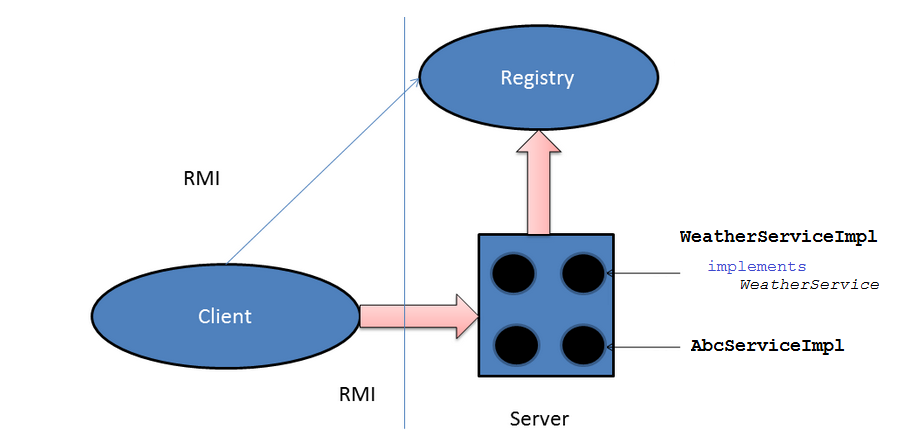
C'est le modèle de travail de RMI. Le serveur enregistrera l'objet avec l'enregistrement (Registry). Le client cherche alors l'enregistrement par adresse IP et Port (Host + Port), afin qu'il puisse appeler des méthodes (method) à partir d'objets dans Serveur.
Constants.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
public class Constants {
public static final String LOCATION_HANOI = "HaNoi";
public static final String LOCATION_TOKYO = "Tokyo";
public static final String LOCATION_CHICAGO = "Chicago";
public static final String WEATHER_RAIN ="rain";
public static final String WEATHER_SUNNY ="sunny";
}WeatherData.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class WeatherData implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Date date;
private String location;
private String weather;
public WeatherData(Date date, String location, String weather) {
this.date = date;
this.location = location;
this.weather = weather;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
}WeatherService.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.Date;
public interface WeatherService extends Remote {
// Method to retrieve weather information.
public WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException;
}WeatherServiceImpl.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class WeatherServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements
WeatherService {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public WeatherServiceImpl() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
@Override
public synchronized WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(date);
int dayOfWeek = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
// Sunday, Monday
if (dayOfWeek == 1 || dayOfWeek == 2) {
if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO)) {
// Rain
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_RAIN);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_HANOI)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_TOKYO)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else {
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
}
}Client.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.client;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Client {
// Host or IP of Server
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Search the registry in the specific Host, Port.
registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(HOST, PORT);
// Lookup WeatherService in the Registry.
WeatherService service = (WeatherService) registry
.lookup(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName());
Date today = new Date();
// Get Chicago weather info:
WeatherData chicagoWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO);
System.out.println("Chicago weather today: "
+ chicagoWeather.getWeather());
// Get Hanoi weather info:
WeatherData hanoiWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_HANOI);
System.out.println("Hanoi weather today: " + hanoiWeather.getWeather());
}
}Server.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Server {
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void startRegistry() throws RemoteException {
// Create server registry
registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(PORT);
}
public static void registerObject(String name, Remote remoteObj)
throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException {
// Bind the object in the registry.
// It is bind with certain name.
// Client will lookup on the registration of the name to get object.
registry.bind(name, remoteObj);
System.out.println("Registered: " + name + " -> "
+ remoteObj.getClass().getName() + "[" + remoteObj + "]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Server starting...");
startRegistry();
registerObject(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName(), new WeatherServiceImpl());
// Server was the start, and was listening to the request from the client.
System.out.println("Server started!");
}
}3. Exécuter l'application
Để chạy được ứng dụng trên bạn cần đóng gói project thành 2 file jar. File jar 1 gồm các class dùng để chạy ứng dụng tại client. Và file jar 2 bao gồm các class để chạy ứng dụng tại server.
Pour exécuter l'application RMI, vous devez emballer votre projet dans deux fichiers jar. Le premier fichier jar comprend des classes à exécuter dans la machine cliente. Et le second fichier jar comprend des classes à exécuter dans la machine serveur.
Pour exécuter l'application RMI, vous devez emballer votre projet dans deux fichiers jar. Le premier fichier jar comprend des classes à exécuter dans la machine cliente. Et le second fichier jar comprend des classes à exécuter dans la machine serveur.
C'est l'illustration:
Cependant vous pouvez exécuter la démo (demo) sur Eclipse:
D'abord, exécuter la classe Server:
Server starting...
Registered: WeatherService -> org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server.WeatherServiceImpl[WeatherServiceImpl[UnicastServerRef [liveRef: [endpoint:[192.168.0.102:64865](local),objID:[6aadac58:179707abf4c:-7fff, -728182817779393915]]]]]
Server started!Le serveur est en cours d'exécution et il enregistre Remote Object avec l'enregistrement (Registry). Ensuite, vous exécutez la classe dans Client.
Chicago weather today: sunny
Hanoi weather today: sunnyJava Basic
- Personnaliser le compilateur Java pour traiter votre annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Programmation Java pour l'équipe utilisant Eclipse et SVN
- Le Tutoriel de Java WeakReference
- Le Tutoriel de Java PhantomReference
- Tutoriel sur la compression et la décompression Java
- Configuration d'Eclipse pour utiliser le JDK au lieu de JRE
- Méthodes Java String.format() et printf()
- Syntaxe et nouvelles fonctionnalités de Java 8
- Expression régulière en Java
- Tutoriel de programmation Java multithreading
- Bibliothèques de pilotes JDBC pour différents types de bases de données en Java
- Tutoriel Java JDBC
- Obtenir des valeurs de colonne automatiquement incrémentées lors de l'insertion d'un enregistrement à l'aide de JDBC
- Le Tutoriel de Java Stream
- Le Tutoriel de Java Functional Interface
- Introduction à Raspberry Pi
- Le Tutoriel de Java Predicate
- Classe abstraite et interface en Java
- Modificateurs d'accès en Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java Enum
- Le Tutoriel de Java Annotation
- Comparer et trier en Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java String, StringBuffer et StringBuilder
- Tutoriel de gestion des exceptions Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java Generics
- Manipulation de fichiers et de répertoires en Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java BiPredicate
- Le Tutoriel de Java Consumer
- Le Tutoriel de Java BiConsumer
- Qu'est-ce qui est nécessaire pour commencer avec Java?
- L'histoire de Java et la différence entre Oracle JDK et OpenJDK
- Installer Java sur Windows
- Installer Java sur Ubuntu
- Installer OpenJDK sur Ubuntu
- Installer Eclipse
- Installer Eclipse sur Ubuntu
- Le Tutoriel Java pour débutant
- Histoire des bits et des bytes en informatique
- Types de données dans Java
- Opérations sur les bits
- Le Tutoriel de instruction Java If else
- Le Tutoriel de instruction Java Switch
- Les Boucles en Java
- Les Tableaux (Array) en Java
- JDK Javadoc au format CHM
- Héritage et polymorphisme en Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java Function
- Le Tutoriel de Java BiFunction
- Exemple de Java encoding et decoding utilisant Apache Base64
- Le Tutoriel de Java Reflection
- Invocation de méthode à distance en Java
- Le Tutoriel de Java Socket
- Quelle plate-forme devez-vous choisir pour développer des applications de bureau Java?
- Le Tutoriel de Java Commons IO
- Le Tutoriel de Java Commons Email
- Le Tutoriel de Java Commons Logging
- Comprendre Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode et Object.equals
- Le Tutoriel de Java SoftReference
- Le Tutoriel de Java Supplier
- Programmation orientée aspect Java avec AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Tutoriels de programmation Java Servlet/JSP
- Tutoriels de Java Collections Framework
- Tutoriels Java API pour HTML & XML
- Tutoriels Java IO
- Tutoriels Java Date Time
- Tutoriels Spring Boot
- Tutoriels Maven
- Tutoriels Gradle
- Tutoriels Java Web Service
- Tutoriels de programmation Java SWT
- Tutoriels de JavaFX
- Tutoriels Java Oracle ADF
- Tutoriels Struts2
- Tutoriels Spring Cloud