Le exemple de Upload file avec Spring Boot et AngularJS
1. Objectif de leçon
Dans cette leçon, je vais vous donner des instruction comment créer une application Upload File à l'aide de Spring Boot et AngularJS, ci-dessous sont des images avant première que nous nous effectuerons :
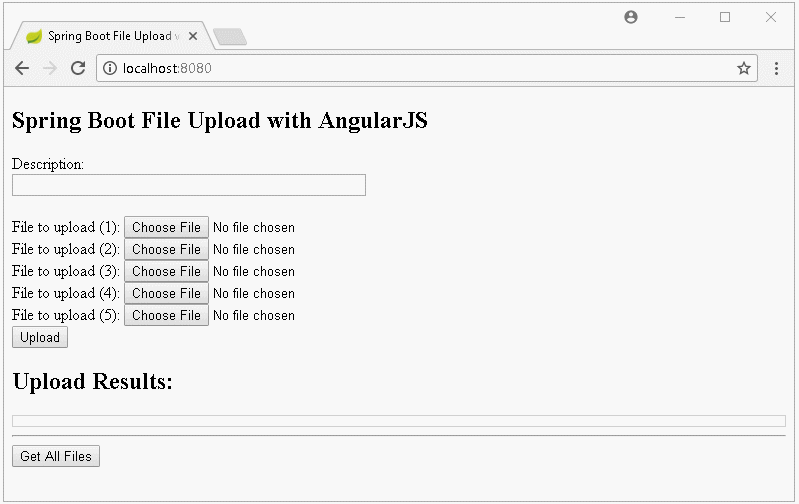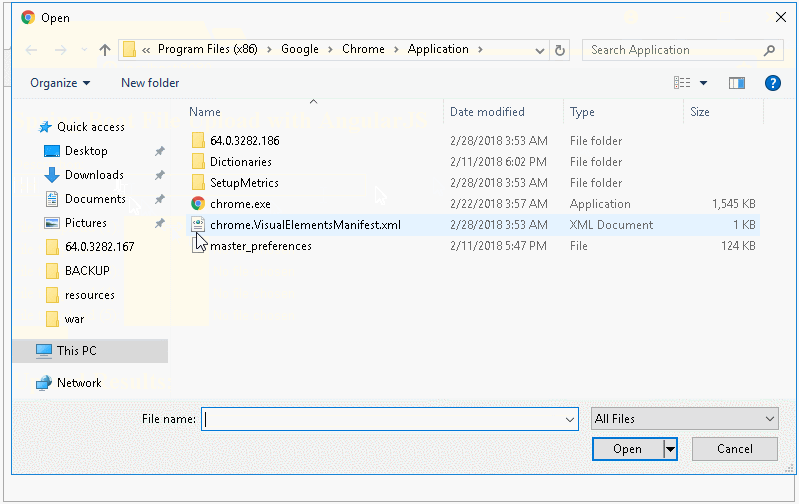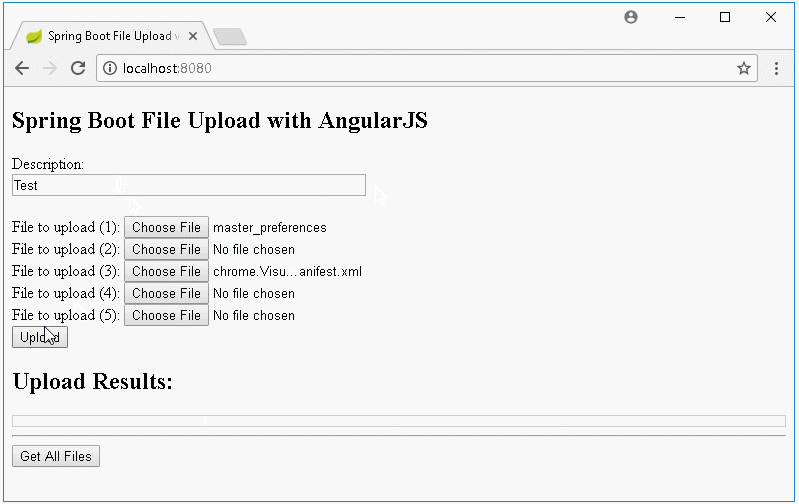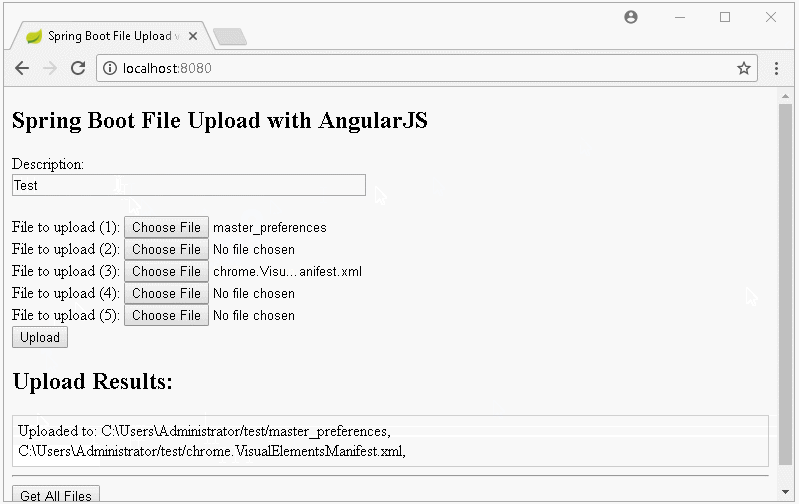
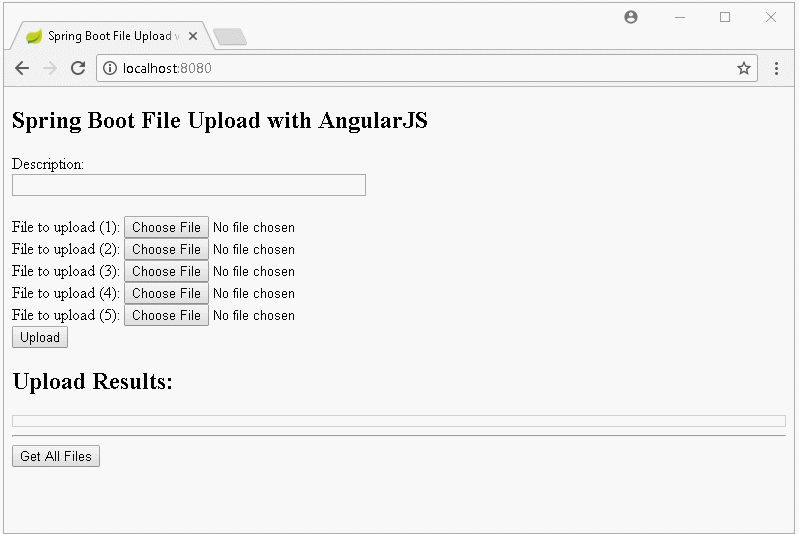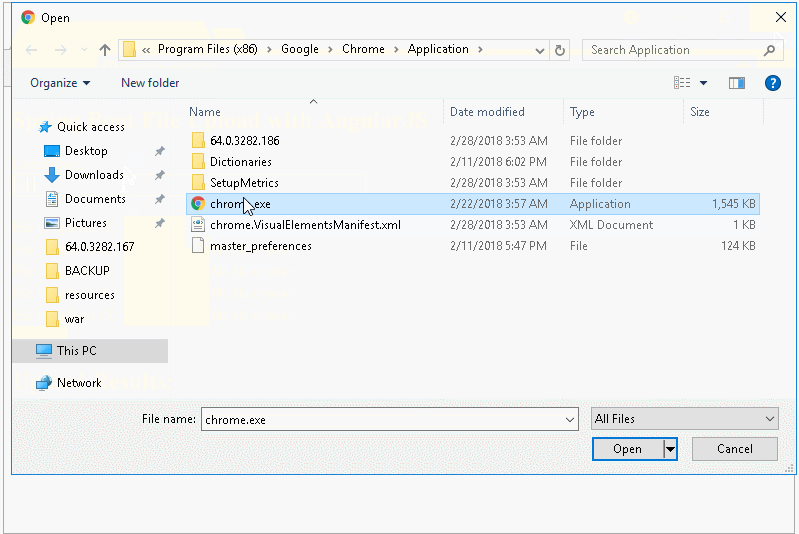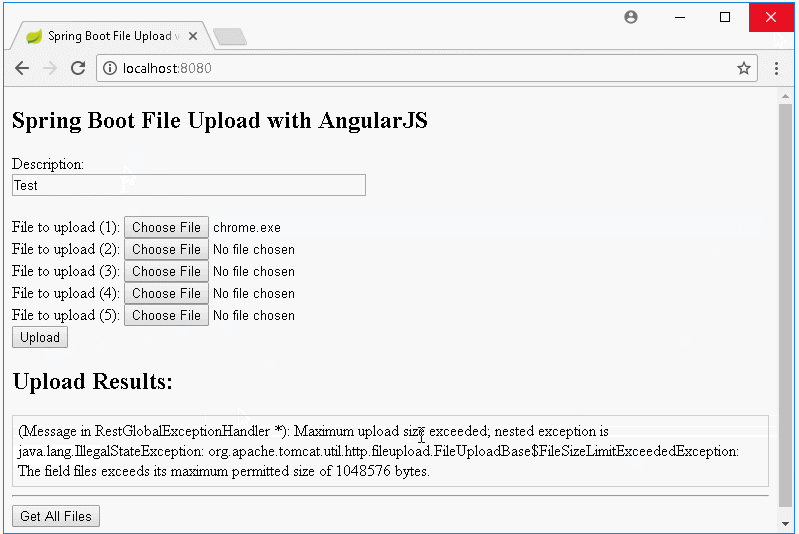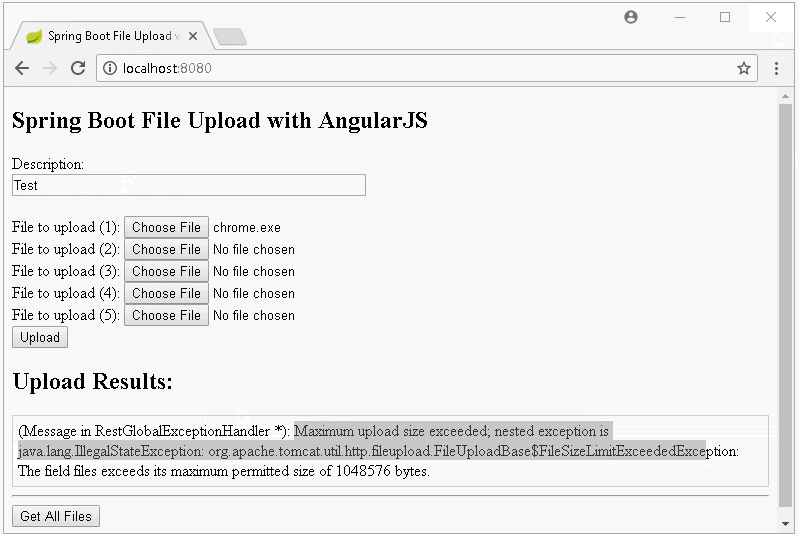
Informez sur l'interface lorsque le téléchargement n'est échoué :
Affichez la liste des fichiers téléchargés et gérez le téléchargement lorsqu'un utilisateur clique sur un lien (link).
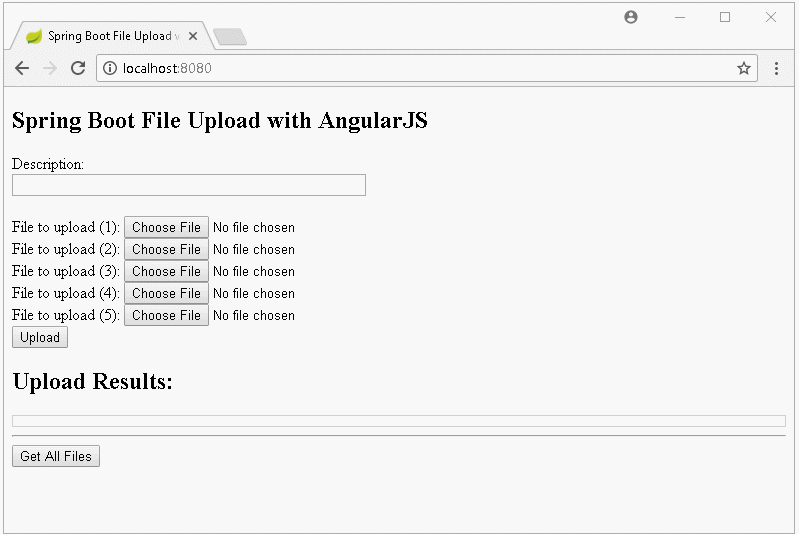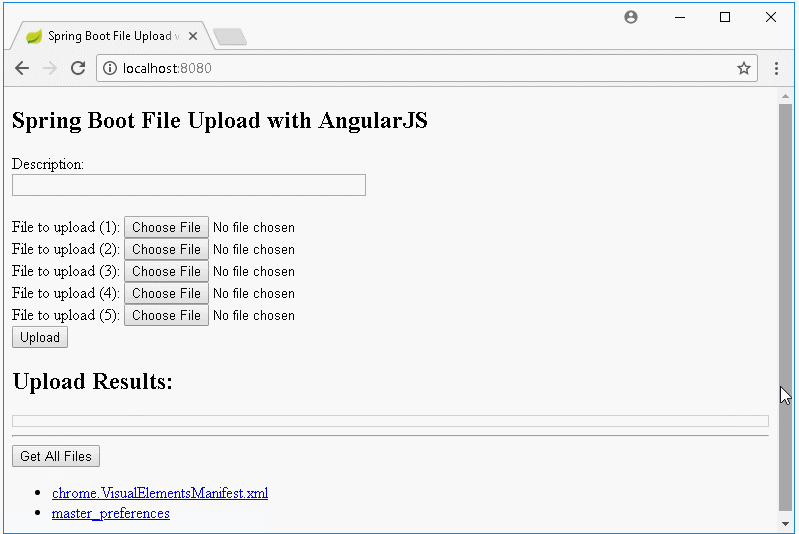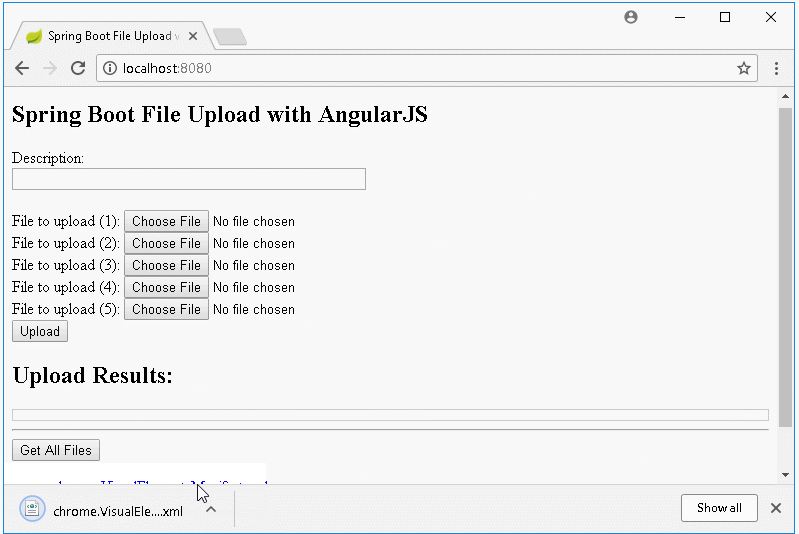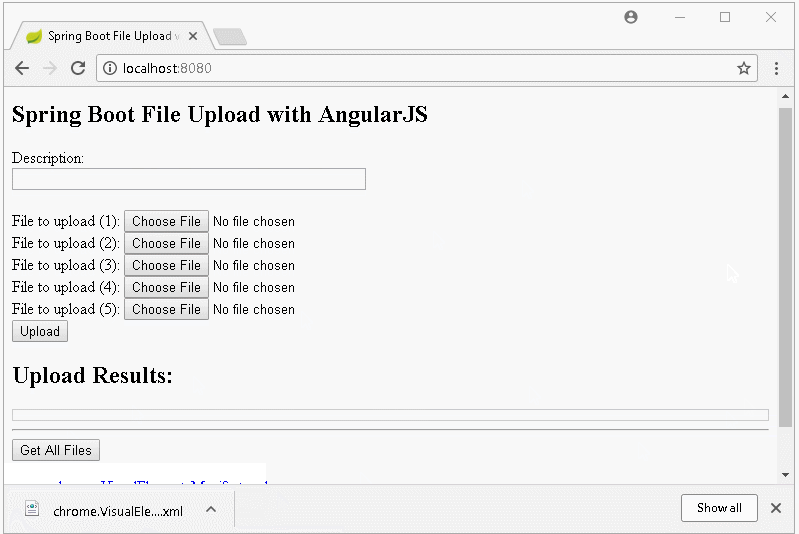
2. Créer un projet Spring Boot
Sur Eclipse créez un projet Spring Boot:
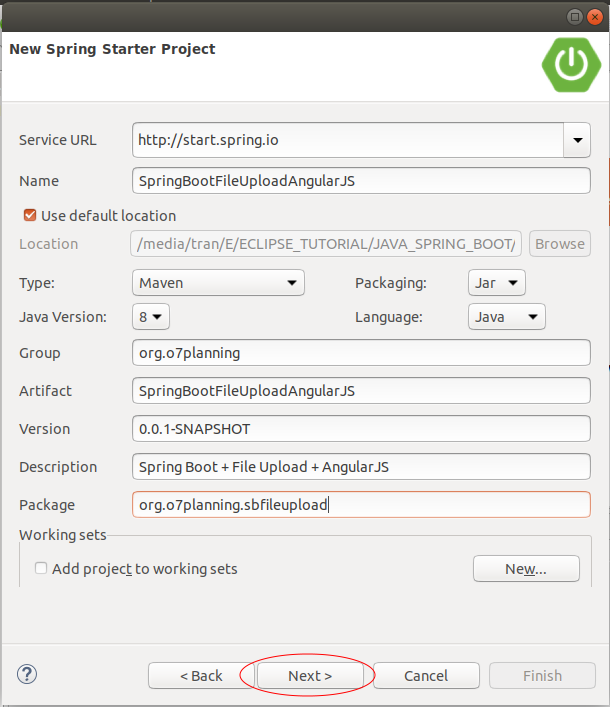
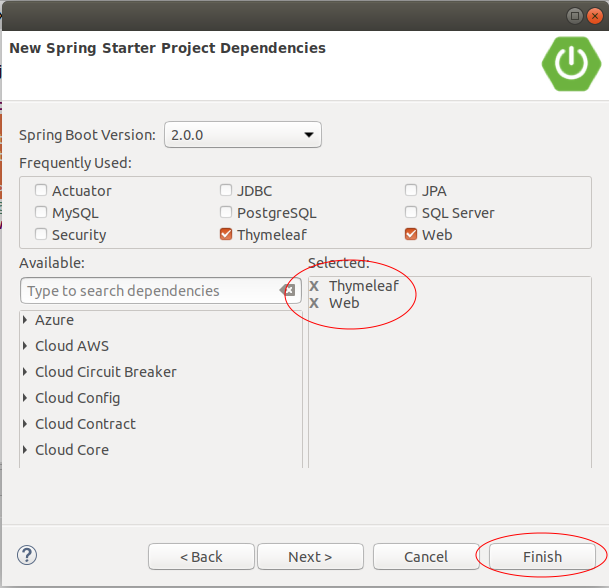
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootFileUploadAngularJS</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootFileUploadAngularJS</name>
<description>Spring Boot + File Upload + AngularJS</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>SpringBootFileUploadAngularJsApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbfileupload;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootFileUploadAngularJsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootFileUploadAngularJsApplication.class, args);
}
}3. Form, Controller, Exception Handler
La classe UploadForm représente les données du form HTML.
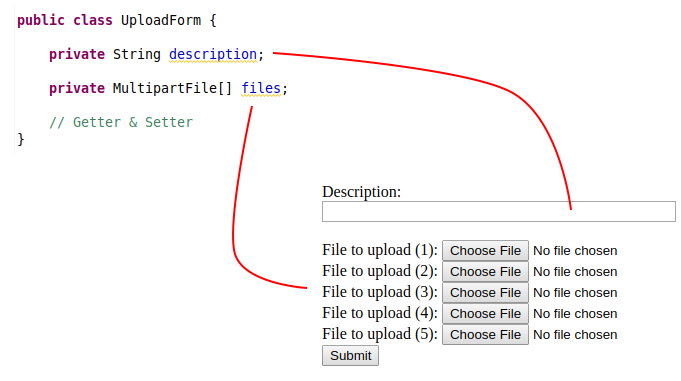
UploadForm.java
package org.o7planning.sbfileupload.form;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
public class UploadForm {
private String description;
private MultipartFile[] files;
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public MultipartFile[] getFiles() {
return files;
}
public void setFiles(MultipartFile[] files) {
this.files = files;
}
}MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbfileupload.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "upload";
}
}La classe MainRESTController définit REST API pour gérer les données des fichiers téléchargés par des utilisateurs. Ces REST API seront appelés par AngularJS (Voir plus dans UploadFileCtrl.js).
MainRESTController.java
package org.o7planning.sbfileupload.restcontroller;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbfileupload.form.UploadForm;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
@RestController
public class MainRESTController {
// Linux: /home/{user}/test
// Windows: C:/Users/{user}/test
private static String UPLOAD_DIR = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/test";
@PostMapping("/rest/uploadMultiFiles")
public ResponseEntity<?> uploadFileMulti(@ModelAttribute UploadForm form) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Description:" + form.getDescription());
String result = null;
try {
result = this.saveUploadedFiles(form.getFiles());
}
// Here Catch IOException only.
// Other Exceptions catch by RestGlobalExceptionHandler class.
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return new ResponseEntity<>("Error: " + e.getMessage(), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
return new ResponseEntity<String>("Uploaded to: " + result, HttpStatus.OK);
}
// Save Files
private String saveUploadedFiles(MultipartFile[] files) throws IOException {
// Make sure directory exists!
File uploadDir = new File(UPLOAD_DIR);
uploadDir.mkdirs();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (MultipartFile file : files) {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
String uploadFilePath = UPLOAD_DIR + "/" + file.getOriginalFilename();
byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
Path path = Paths.get(uploadFilePath);
Files.write(path, bytes);
sb.append(uploadFilePath).append(", ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
@GetMapping("/rest/getAllFiles")
public List<String> getListFiles() {
File uploadDir = new File(UPLOAD_DIR);
File[] files = uploadDir.listFiles();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (File file : files) {
list.add(file.getName());
}
return list;
}
// @filename: abc.zip,..
@GetMapping("/rest/files/{filename:.+}")
public ResponseEntity<Resource> getFile(@PathVariable String filename) throws MalformedURLException {
File file = new File(UPLOAD_DIR + "/" + filename);
if (!file.exists()) {
throw new RuntimeException("File not found");
}
Resource resource = new UrlResource(file.toURI());
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "attachment; filename=\"" + file.getName() + "\"")
.body(resource);
}
}La capacité par défaut du fichier téléchargé sur le Serveur se limite de 1MB. Et si un utilisateur télécharge plusieurs fichiers en même temps, la capacité totale de ces fichiers ne peut pas dépasser 1MB. Pourtant vous pouvez également configurer afin de changer ces paramètres.
application.properties
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=1MB
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=5MB
spring.thymeleaf.cache=falseRestGlobalExceptionHandler est une classe personnalisée, étendue de la classe ResponseEntityExceptionHandler. Dans ce cas, vous pouvez gérer des exceptions jetée (throw) à partir des méthodes REST. Ceci vous aide à se concentrer à une seule location au lieu de gérer une exception pour chaque méthode REST.
RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package org.o7planning.sbfileupload.exceptionhandler;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
// Catch max file size Exception.
@ExceptionHandler(MultipartException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<?> handleControllerException(HttpServletRequest request, Throwable ex) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<String>("(Message in RestGlobalExceptionHandler *): " + ex.getMessage(), status);
}
// Catch Other Exception
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<?> handleControllerRootException(HttpServletRequest request, Throwable ex) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<String>("(Message in RestGlobalExceptionHandler **): " + ex.getMessage(), status);
}
private HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (statusCode == null) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode);
}
}4. Javascript & View (Thymeleaf)
upload.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Spring Boot File Upload with AngularJS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<!-- Check other AngularJS version at: -->
<!-- https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/docs/misc/downloading -->
<script
src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.6.9/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="/js/MainApp.js"></script>
<script src="/js/UploadFileCtrl.js"></script>
<script src="/js/GetFilesCtrl.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="MainApp">
<h2>Spring Boot File Upload with AngularJS</h2>
<div ng-controller="UploadFileController">
<form>
Description: <br/>
<input type="text" name="description" ng-model="myForm.description" style="width:350px;"/>
<br/><br/>
File to upload (1): <input type="file" file-model="myForm.files[0]"/><br />
File to upload (2): <input type="file" file-model="myForm.files[1]"/><br />
File to upload (3): <input type="file" file-model="myForm.files[2]"/><br />
File to upload (4): <input type="file" file-model="myForm.files[3]"/><br />
File to upload (5): <input type="file" file-model="myForm.files[4]"/><br />
<button type="button" ng-click="doUploadFile()">Upload</button>
</form>
<h2>Upload Results:</h2>
<div style="border:1px solid #ccc;padding: 5px;">
<span ng-bind="uploadResult"></span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Get Files -->
<hr>
<div ng-controller="GetFilesController">
<button type="button" ng-click="getAllFiles()">Get All Files</button>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="file in allFiles">
<a href='/rest/files/{{file}}'>{{file}}</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>Dans AngularJS, l'utilisation de l'attribuut (attribute) ng-model vous aide à contraindre deux voies (2-way binding) entre l'élément Input de Form et celui de Model, c'ét-à-dire, si les données sur Model changent, l'élément (l'élément Input) sera mis à jour, et vice versa, si un utilisateur change l'interface de (l'élément Input) Model sera mis à jour.
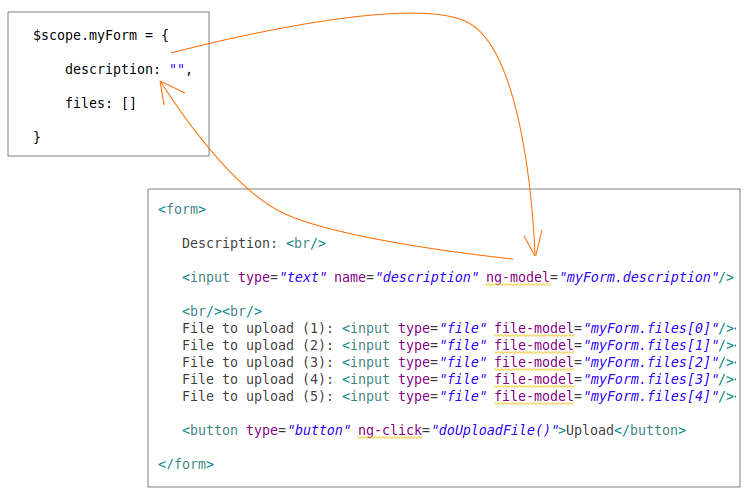
Malheureusement, l'attribut (attribute) ng-model ne fournit pas la contrainte entre Model et Input[file], donc vous devez définir une directive baptisée "fileModel" afin de contraindre deux voies entre Model et Input[file]. Cette Directive est définit dans MainApp.js :
js/MainApp.js
// main app.
var mainApp = angular.module('MainApp', []);
// DIRECTIVE - FILE MODEL
mainApp.directive('fileModel', ['$parse', function ($parse) {
return {
restrict: 'A',
link: function(scope, element, attrs) {
var model = $parse(attrs.fileModel);
var modelSetter = model.assign;
element.bind('change', function(){
scope.$apply(function(){
modelSetter(scope, element[0].files[0]);
});
});
}
};
}]);The UploadFileCtrl.js file contains AngularJS functions to control uploading files to the Server.
js/UploadFileCtrl.js
// CONTROLLER UPLOAD FILE
mainApp.controller('UploadFileController', function($scope, $http) {
$scope.uploadResult ="";
$scope.myForm = {
description: "",
files: []
}
$scope.doUploadFile = function() {
var url = "/rest/uploadMultiFiles";
var data = new FormData();
data.append("description", $scope.myForm.description);
for (i = 0; i < $scope.myForm.files.length; i++) {
data.append("files", $scope.myForm.files[i]);
}
var config = {
transformRequest: angular.identity,
transformResponse: angular.identity,
headers: {
'Content-Type': undefined
}
}
$http.post(url, data, config).then(
// Success
function(response) {
$scope.uploadResult = response.data;
},
// Error
function(response) {
$scope.uploadResult = response.data;
});
};
});Le fichier GetFilesCtrl.js comprend les fonctions AngularJS afin de controler l'obtention de la liste des fichiers téléchargé sur Server.
js/GetFilesCtrl.js
mainApp.controller('GetFilesController', function($scope, $http) {
$scope.allFiles = [];
$scope.getAllFiles = function() {
// REST URL:
var url = "/rest/getAllFiles";
$http.get(url).then(
// Success
function(response) { alert("OK");
$scope.allFiles = response.data;
},
// Error
function(response) {
alert("Error: " + response.data);
}
);
};
});Tutoriels Spring Boot
- Installer Spring Tool Suite pour Eclipse
- Le Tutoriel de Spring pour débutant
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot pour débutant
- Propriétés communes de Spring Boot
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et Thymeleaf
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et FreeMarker
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et Groovy
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et Mustache
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et JSP
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Utiliser Logging dans Spring Boot
- Surveillance des applications avec Spring Boot Actuator
- Créer une application Web multilingue avec Spring Boot
- Utiliser plusieurs ViewResolvers dans Spring Boot
- Utiliser Twitter Bootstrap dans Spring Boot
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot Interceptor
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot, Spring JDBC et Spring Transaction
- Le Tutoriel de Spring JDBC
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot, JPA et Spring Transaction
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et Spring Data JPA
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot, Hibernate et Spring Transaction
- Intégration de Spring Spring, JPA et H2 Database
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Boot et MongoDB
- Utiliser plusieurs DataSources avec Spring Boot et JPA
- Utiliser plusieurs DataSources avec Spring Boot et RoutingDataSource
- Créer une application de connexion avec Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Créer une application de connexion avec Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Créer une application d'enregistrement d'utilisateur avec Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Exemple de OAuth2 Social Login dans Spring Boot
- Exécuter des tâches planifiées en arrière-plan dans Spring
- Exemple CRUD Restful WebService avec Spring Boot
- Exemple Spring Boot Restful Client avec RestTemplate
- Exemple CRUD avec Spring Boot, REST et AngularJS
- Sécurité Spring RESTful Service utilisant Basic Authentication
- Sécuriser Spring Boot RESTful Service en utilisant Auth0 JWT
- Exemple Upload file avec Spring Boot
- Le exemple de Download file avec Spring Boot
- Le exemple de Upload file avec Spring Boot et jQuery Ajax
- Le exemple de Upload file avec Spring Boot et AngularJS
- Créer une application Web Panier avec Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Le Tutoriel de Spring Email
- Créer une application Chat simple avec Spring Boot et Websocket
- Déployer le application Spring Boot sur Tomcat Server
- Déployer le application Spring Boot sur Oracle WebLogic Server
- Installer un certificat SSL gratuit Let's Encrypt pour Spring Boot
- Configurer Spring Boot pour rediriger HTTP vers HTTPS
Show More