Lire et écrire un fichier Excel en Java à l'aide d'Apache POI
1. Qu'est-ce que POI d'Apache ?
Apache POI est une bibliothèque Java open source fournie par Apache, c'est la puissante bibliothèque pour vous aider à travailler avec des documents Microsoft tels que Word, Excel, Powerpoint, Visio,....
POI singnifie "Poor Obfuscation Implementation". Les formats de fichiers de Microsoft sont fermés. Les ingénieurs d'Apache ont essayé de l'apprendre , et ils voient que Microsoft a créé le format complexe inutile. Et le nom est dérivé de l'humour bibliothèque.
Poor Obfuscation Implementation: Réalise l'insensé. (Traduit approximative en tant que telle).
POI singnifie "Poor Obfuscation Implementation". Les formats de fichiers de Microsoft sont fermés. Les ingénieurs d'Apache ont essayé de l'apprendre , et ils voient que Microsoft a créé le format complexe inutile. Et le nom est dérivé de l'humour bibliothèque.
Poor Obfuscation Implementation: Réalise l'insensé. (Traduit approximative en tant que telle).
Dans cette publication, je vous donnerai les instruction d'usage de Apache POI lorsque vous travaillez avec Excel.
2. Vue d'ensemble de Apache POI
Apache POI vous permet de travailler avec les format de Microsoft, ses classes sont habituellement préfixes avec HSSF, XSSF, HPSF,... Regardez le préfixe d'une classe, vous pouvez savoir quel type de format qu'elle soutient.
Par exemple, afin de travailler avec le format Excel (XLS) vous avez besoin des classes :
- HSSFWorkbook
- HSSFSheet
- HSSFCellStyle
- HSSFDataFormat
- HSSFFont
- ...
Prefix | Description | |
1 | HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) | reads and writes Microsoft Excel (XLS) format files. |
2 | XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) | reads and writes Office Open XML (XLSX) format files. |
3 | HPSF (Horrible Property Set Format) | reads “Document Summary” information from Microsoft Office files. |
4 | HWPF (Horrible Word Processor Format) | aims to read and write Microsoft Word 97 (DOC) format files. |
5 | HSLF (Horrible Slide Layout Format) | a pure Java implementation for Microsoft PowerPoint files. |
6 | HDGF (Horrible DiaGram Format) | an initial pure Java implementation for Microsoft Visio binary files. |
7 | HPBF (Horrible PuBlisher Format) | a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Publisher files. |
8 | HSMF (Horrible Stupid Mail Format) | a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Outlook MSG files |
9 | DDF (Dreadful Drawing Format) | a package for decoding the Microsoft Office Drawing format. |
3. Vue d'ensemble de Apache POI Excel
L'image ci-dessous illustre la structure d'un document Excel.
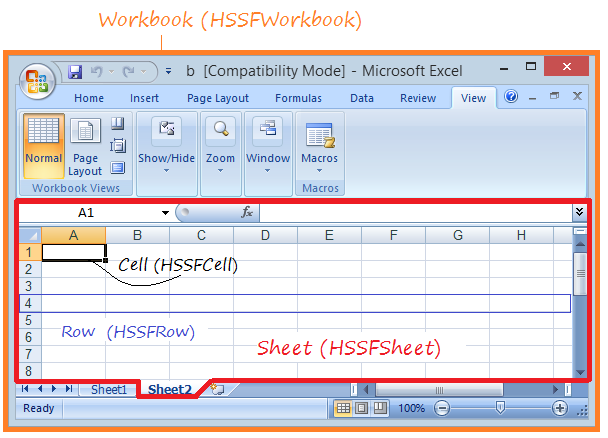
Apache POI vous fournit quelques interfaces Workbook, Sheet, Row, Cell,... et des classes d'implementation sont respectivement HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow, HSSFCell,...
4. Bibliothèque de Apache POI
Si votre projet utilise Maven, vous devez seulement déclarer la bibliothèque dans le pom.xml de la manière simple :
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>Si vous n'utilisez pas de Maven, vous pouvez télécharger la bibliothèque Apache POIà :
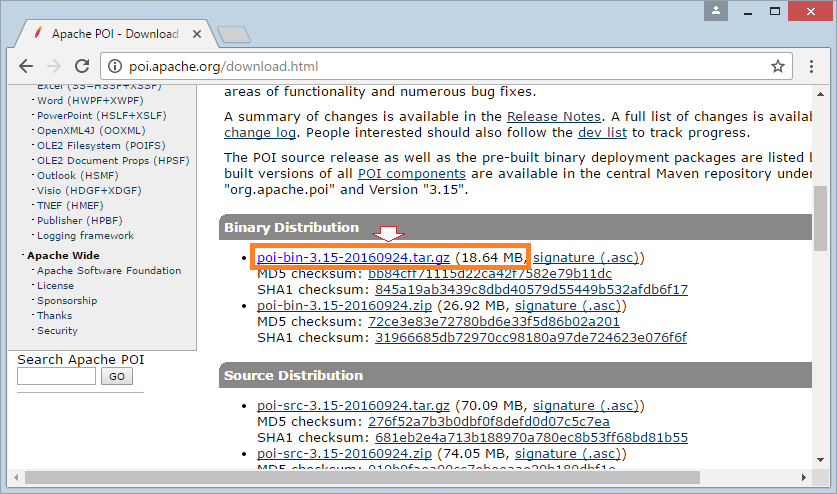
Téléchargez et décompressez-le, afin de travailler avec Excel, il faut au moins trois fichiers jar :
- poi-**.jar
- lib/commons-codec-**.jar
- lib/commons-collections4-**.jar
Dans cette publication, j'ai créé un projet Maven simple avec le nom ApachePOIExcel
- Group ID: org.o7planning
- Artifact ID: ApachePOIExcel
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>ApachePOIExcel</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>5. Créer et écrire des fichiers Excel
Dans les versions antérieures de Microsoft Office (97-2003), les fichiers excel ont le format XLS et dans la version actuelle, le format XSLX est souvent utilisé. Pour travailler avec le fichier XSLX, vous devez utiliser des classes avec le préfixe XSSF.
Ci-dessous est un exemple simple en utilisant le POI pour créer un fichier Excel. Vous pouvez combiner avec l'utilisation de style sur la cellule (Cell) pour créer un meilleur document Excel.POI Style est mentionné plus en détail à la fin du document.
CreateExcelDemo.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellType;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.model.Employee;
import org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.model.EmployeeDAO;
public class CreateExcelDemo {
private static HSSFCellStyle createStyleForTitle(HSSFWorkbook workbook) {
HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBold(true);
HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employees sheet");
List<Employee> list = EmployeeDAO.listEmployees();
int rownum = 0;
Cell cell;
Row row;
//
HSSFCellStyle style = createStyleForTitle(workbook);
row = sheet.createRow(rownum);
// EmpNo
cell = row.createCell(0, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("EmpNo");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// EmpName
cell = row.createCell(1, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("EmpNo");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Salary
cell = row.createCell(2, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("Salary");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Grade
cell = row.createCell(3, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("Grade");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Bonus
cell = row.createCell(4, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue("Bonus");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
// Data
for (Employee emp : list) {
rownum++;
row = sheet.createRow(rownum);
// EmpNo (A)
cell = row.createCell(0, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue(emp.getEmpNo());
// EmpName (B)
cell = row.createCell(1, CellType.STRING);
cell.setCellValue(emp.getEmpName());
// Salary (C)
cell = row.createCell(2, CellType.NUMERIC);
cell.setCellValue(emp.getSalary());
// Grade (D)
cell = row.createCell(3, CellType.NUMERIC);
cell.setCellValue(emp.getGrade());
// Bonus (E)
String formula = "0.1*C" + (rownum + 1) + "*D" + (rownum + 1);
cell = row.createCell(4, CellType.FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula(formula);
}
File file = new File("C:/demo/employee.xls");
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
FileOutputStream outFile = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(outFile);
System.out.println("Created file: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}Employee.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.model;
public class Employee {
private String empNo;
private String empName;
private Double salary;
private int grade;
private Double bonus;
public Employee(String empNo, String empName,//
Double salary, int grade, Double bonus) {
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.salary = salary;
this.grade = grade;
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public String getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(String empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public Double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public Double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(Double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}EmployeeDAO.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class EmployeeDAO {
public static List<Employee> listEmployees() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Employee e1 = new Employee("E01", "Tom", 200.0, 1, null);
Employee e2 = new Employee("E02", "Jerry", 100.2, 2, null);
Employee e3 = new Employee("E03", "Donald", 150.0, 2, null);
list.add(e1);
list.add(e2);
list.add(e3);
return list;
}
}Exécutez l'exemple :
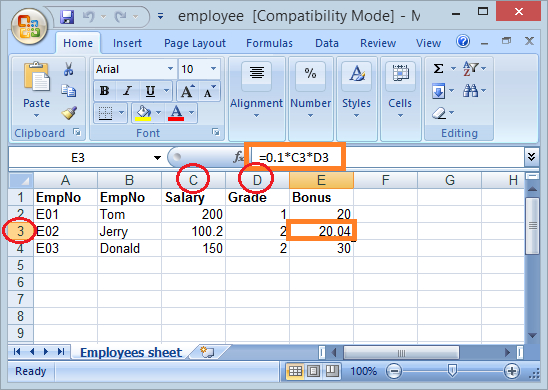
6. Lire fichier xsl et xslx
L'exemple ci-dessous lit un simple fichier excel et imprime les informations à l'écran de la Console. Le fichier excel utilisé pour lire est créé dans l'exemple ci-dessus.
Remarque : Dans cet article, j'utilise Apache POI 3.15 , l'API a beaucoup de changements par rapport à l'ancienne version. Il y a beaucoup de méthodes qui seront supprimées dans la future version (Apache POI 4.x). Le POI va de l'avant avec l'utilisation d'Enum pour remplacer les constantes dans son API.
ReadExcelDemo.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellType;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.FormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
public class ReadExcelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Read XSL file
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("C:/demo/employee.xls"));
// Get the workbook instance for XLS file
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
// Get first sheet from the workbook
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
// Get iterator to all cells of current row
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
// Change to getCellType() if using POI 4.x
CellType cellType = cell.getCellTypeEnum();
switch (cellType) {
case _NONE:
System.out.print("");
System.out.print("\t");
break;
case BOOLEAN:
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
System.out.print("\t");
break;
case BLANK:
System.out.print("");
System.out.print("\t");
break;
case FORMULA:
// Formula
System.out.print(cell.getCellFormula());
System.out.print("\t");
FormulaEvaluator evaluator = workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
// Print out value evaluated by formula
System.out.print(evaluator.evaluate(cell).getNumberValue());
break;
case NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue());
System.out.print("\t");
break;
case STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue());
System.out.print("\t");
break;
case ERROR:
System.out.print("!");
System.out.print("\t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
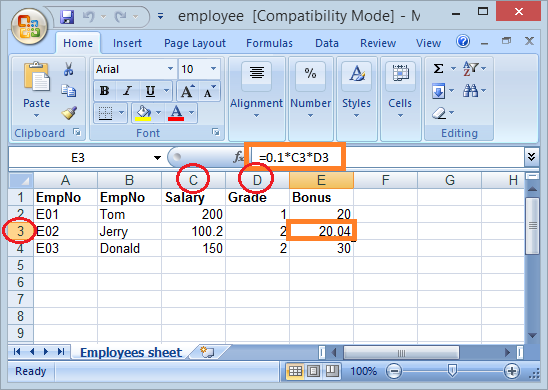
}Exécution de l'exemple :
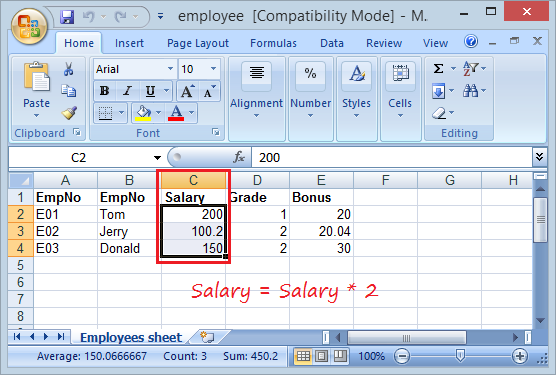
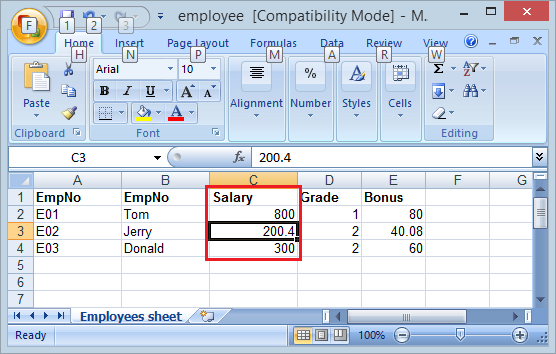
7. Mettre à jour le fichier Excel disponible
Dans cet exemple, je lis file excel employee.xls et mettre à jour les valeurs de la colonne pour celle de Salary a augmenté deux fois.
UpdateExcelDemo.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
public class UpdateExcelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("C:/demo/employee.xls");
// Read XSL file
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// Get the workbook instance for XLS file
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
// Get first sheet from the workbook
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
HSSFCell cell = sheet.getRow(1).getCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2);
cell = sheet.getRow(2).getCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2);
cell = sheet.getRow(3).getCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2);
inputStream.close();
// Write File
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
}
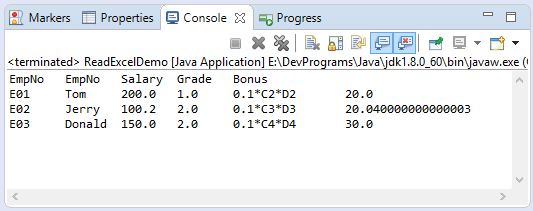
}Résultats après la mise à jour :
8. Formules et évaluation
Si vous avez la connaissance d'Excel, il vous sera facile d'élaborer une formule. Pour Apache POI, vous pouvez créer une Cellule avec CellType.FORMULA, sa valeur est calculée sur une formule.
SUM
Exemple : Compter les cellules sur la même colonne "C" de la 2e à la ligne à 4e:
// Create Cell type of FORMULA
cell = row.createCell(rowIndex, CellType.FORMULA);
// Set formula
cell.setCellFormula("SUM(C2:C4)");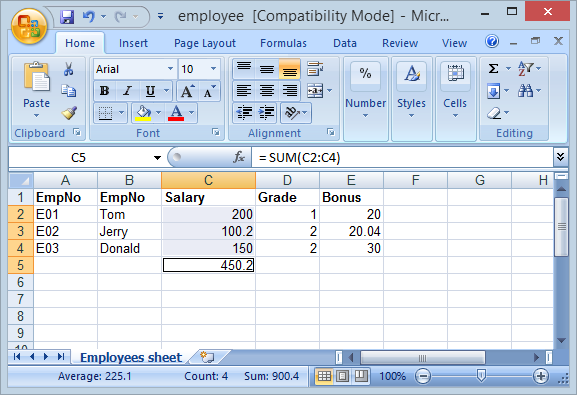
Exemple de formule :
cell = row.createCell(rowIndex, CellType.FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("0.1*C2*D3");Pour une cellule de type FORMULA, vous pouvez imprimer sa formule et utiliser FormulaEvaluator pour calculer la valeur de cellule donnée par la formule.
// Formula
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
FormulaEvaluator evaluator
= workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
// CellValue
CellValue cellValue = evaluator.evaluate(cell);
double value = cellValue.getNumberValue();
String value = cellValue.getStringValue();
boolean value = cellValue.getBooleanValue();
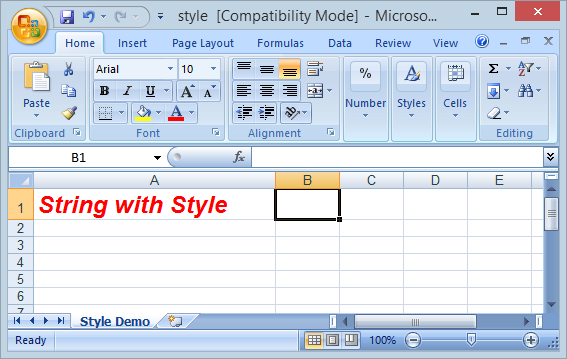
// ...9. Style
Exemple :
StyleDemo.java
package org.o7planning.apachepoiexcel.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors;
public class StyleDemo {
private static HSSFCellStyle getSampleStyle(HSSFWorkbook workbook) {
// Font
HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBold(true);
font.setItalic(true);
// Font Height
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 18);
// Font Color
font.setColor(IndexedColors.RED.index);
// Style
HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Style Demo");
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue("String with Style");
HSSFCellStyle style = getSampleStyle(workbook);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
File file = new File("C:/demo/style.xls");
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
FileOutputStream outFile = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(outFile);
System.out.println("Created file: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}Tutoriels Java Open Source Libraries
- Le Tutoriel de Java JSON Processing API (JSONP)
- Utilisation de l'API Java Scribe OAuth avec Google OAuth2
- Obtenir des informations sur le matériel dans l'application Java
- Restfb Java API pour Facebook
- Créer Credentials pour Google Drive API
- Le Tutoriel de Java JDOM2
- Le Tutoriel de Java XStream
- Utiliser Java Jsoup pour analyser HTML
- Récupérer des informations géographiques basées sur l'adresse IP à l'aide de GeoIP2 Java API
- Lire et écrire un fichier Excel en Java à l'aide d'Apache POI
- Explorer le Facebook Graph API
- Manipulation de fichiers et de dossiers sur Google Drive à l'aide de Java
Show More