Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalAdjuster
1. TemporalAdjuster
L'interface TemporalAdjuster est un outil d'ajustement d'un objet Temporal pour en créer une copie. En règle générale, TemporalAdjuster existe pour externaliser un processus d'ajustement des objets Temporal plutôt que de les ajuster directement.
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TemporalAdjuster {
Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal);
}Par exemple : On crée la classe TruncateTimeAdjuster pour tronquer le temps (heures, minutes, secondes, nanosecondes) d'un objet Temporal.
Temporal | Example | Apply TruncateTimeAdjuster |
LocalDateTime | 2020-11-25 13:30:45 | 2020-11-25 00:00:00 |
ZonedDateTime | 2020-11-25 13:30:45+06:00[Asia/Bishkek] | 2020-11-25 00:00:00+06:00[Asia/Bishkek] |
LocalTime | 13:30:45 | 00:00:00 |
TruncateTimeAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class TruncateTimeAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
Temporal adjustedTemporal = temporal;
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND, 0);
}
return adjustedTemporal;
}
}Utiliser TruncateTemporalAdjuster:
TruncateTimeAdjuster_ex1.java
TruncateTimeAdjuster truncateTimeAdjuster = new TruncateTimeAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime adjustedLocalDateTime = (LocalDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(localDateTime);
System.out.printf("localDateTime: %s%n", localDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedLocalDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedLocalDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = OffsetDateTime.now();
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime = (OffsetDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime: %s%n", offsetDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime: %s%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime);Output:
localDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.309188
adjustedLocalDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.322306+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
offsetDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.323143+06:00
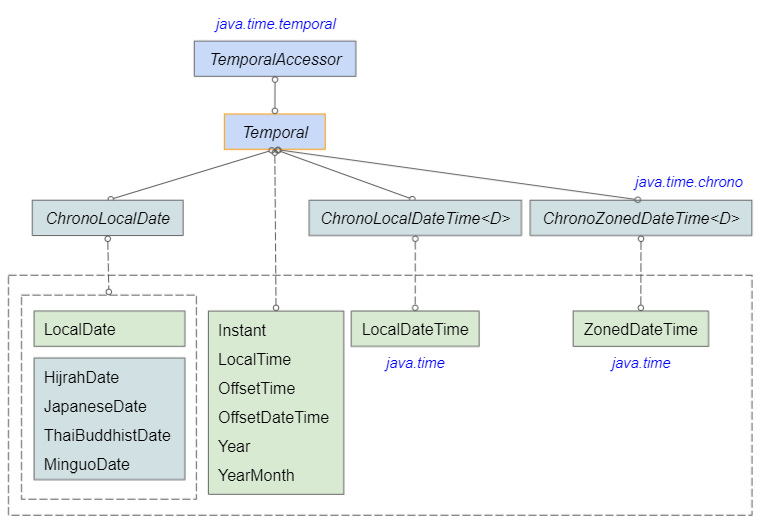
adjustedOffsetDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00+06:00Il existe de nombreuses classes dans Java Date Time API qui implémentent l'interface TemporalAdjuster, ce qui signifie qu'elles sont capables d'ajuster d'autres objets Temporal :
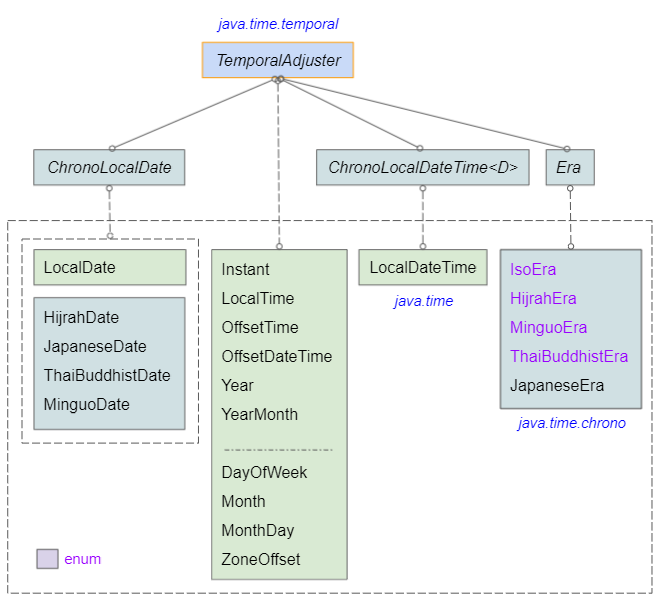
- IsoEra
- MinguoEra
- LocalDateTime
- LocalTime
- ZoneOffset
- HijrahEra
- MonthDay
- Month
- DayOfWeek
- LocalDate
- JapaneseEra
- YearMonth
- OffsetTime
- Instant
- Era
- Year
- OffsetDateTime
- ThaiBuddhistEra
- ChronoLocalDate
- ThaiBuddhistDate
- MinguoDate
- JapaneseDate
- HijrahDate
- ChronoLocalDateTime
- TemporalAdjusters
Il existe deux manières d'ajuster un objet Temporal, dont la deuxième approche est recommandée.
// these two lines are equivalent, but the second approach is recommended
adjustedTemporal = thisAdjuster.adjustInto(temporal); // (1)
adjustedTemporal = temporal.with(thisAdjuster); // (2)2. Basic Examples
Par exemple : Ajuster tous les objets Temporal donnés en mai 2000, les autres champs restent inchangés.
TemporalAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.YearMonth;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class TemporalAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = YearMonth.of(2020, 5); // May 2020.
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate adjustedLocalDate = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate);
System.out.printf("localDate: %s%n", localDate);
System.out.printf("adjustedLocalDate: %s%n", adjustedLocalDate);
}
}Output:
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:51:07.837210+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2020-05-05T00:51:07.837210+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
localDate: 2021-07-05
adjustedLocalDate: 2020-05-05Par exemple: Ajuster la zone de décalage horaire (zone-offset) aux objets OffsetDateTime donnés à +15;
TemporalAdjuster_ex2.java
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = ZoneOffset.ofHours(15);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime1 = OffsetDateTime.now();
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime1 = (OffsetDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime1);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime1: %s%n", offsetDateTime1);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime1: %s%n%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime1);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime2 = OffsetDateTime.parse("2000-01-01T01:00+01:00");
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime2 = (OffsetDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime2);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime2: %s%n", offsetDateTime2);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime2: %s%n%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime2);Output:
offsetDateTime1: 2021-07-05T01:15:48.372665+06:00
adjustedOffsetDateTime1: 2021-07-05T01:15:48.372665+15:00
offsetDateTime2: 2000-01-01T01:00+01:00
adjustedOffsetDateTime2: 2000-01-01T01:00+15:00- OffsetDateTime
- ZonedDateTime
- LocalDate
3. Custom TemporalAdjuster Examples
On suppose que les jours ouvrables de la semaine soient du lundi au vendredi. On écrit la classe NextWorkingDayAdjuster pour trouver le prochain jour ouvrable après la date donnée.
NextWorkingDayAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextWorkingDayAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
int field = temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK);
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = DayOfWeek.of(field);
int daysToAdd = 1;
if (DayOfWeek.FRIDAY.equals(dayOfWeek)) {
daysToAdd = 3;
} else if (DayOfWeek.SATURDAY.equals(dayOfWeek)) {
daysToAdd = 2;
}
return temporal.plus(daysToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
}
}Par exemple: utiliser la classe NextWorkingDayAdjuster:
NextWorkingDayAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextWorkingDayAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = new NextWorkingDayAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate nextWorkingDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate);
System.out.printf("localDate: %s%n", localDate);
System.out.printf("nextWorkingDay: %s%n", nextWorkingDay);
System.out.println(" ----- ");
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
nextWorkingDay = adjustedZonedDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("nextWorkingDay: %s%n", nextWorkingDay);
}
}Output:
localDate: 2021-07-05
nextWorkingDay: 2021-07-06
-----
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T01:34:09.112648+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2021-07-06T01:34:09.112648+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
nextWorkingDay: 2021-07-06Par exemple : Écrire la classe NextChristmasAdjuster pour trouver la prochaine date de Noël :
NextChristmasAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextChristmasAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
int month = temporal.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR);
int day = temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
if(month == 12 && day > 25) {
temporal = temporal.plus(Period.ofYears(1));
}
return temporal.with(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 12).with(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 25);
}
}Utiliser la classe NextChristmasAdjuster:
NextChristmasAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextChristmasAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = new NextChristmasAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2021, 7, 5);
LocalDate nextChristmasDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate1);
System.out.printf("localDate1: %s%n", localDate1);
System.out.printf("nextChristmasDay: %s%n", nextChristmasDay);
System.out.println(" ----- ");
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate2 = LocalDate.of(2021, 12, 26);
nextChristmasDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate2);
System.out.printf("localDate2: %s%n", localDate2);
System.out.printf("nextChristmasDay: %s%n", nextChristmasDay);
}
}Output:
localDate1: 2021-07-05
nextChristmasDay: 2021-12-25
-----
localDate2: 2021-12-26
nextChristmasDay: 2022-12-25- ChronoField
- Temporal
- ZonedDateTime
- DayOfWeek
4. TemporalAdjusters Examples
La classe TemporalAdjusters fournit des méthodes statiques pour obtenir le(s) TemporalAdjuster(s) standard. Ils comprennent :
- Trouver le premier ou le dernier jour du mois.
- Trouver le premier jour du mois prochain.
- Trouver le premier ou le dernier jour de l'année.
- Trouver le premier jour de l'année prochaine.
- Recherche du premier ou du dernier "jour de la semaine" dans un mois, par exemple "premier mercredi de juin".
- Recherche du "jour de la semaine" suivant ou précédent, tel que "jeudi prochain".
Tutoriels Java Date Time
- Le Tutoriel de Java ZoneId
- Le Tutoriel de Java Temporal
- Le Tutoriel de Java Period
- Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalAdjusters
- Le Tutoriel de Java MinguoDate
- Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalAccessor
- Le Tutoriel de Java JapaneseEra
- Le Tutoriel de Java HijrahDate
- Le Tutoriel de Java Date, Time
- Qu'est-ce que l'heure d'été (DST)?
- Le Tutoriel de Java LocalDate
- Le Tutoriel de Java LocalTime
- Le Tutoriel de Java LocalDateTime
- Le Tutoriel de Java ZonedDateTime
- Le Tutoriel de Java JapaneseDate
- Le Tutoriel de Java Duration
- Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalQuery
- Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalAdjuster
- Le Tutoriel de Java ChronoUnit
- Le Tutoriel de Java TemporalQueries
Show More
- Tutoriels Java Web Service
- Tutoriels de programmation Java Servlet/JSP
- Tutoriels de JavaFX
- Tutoriels de programmation Java SWT
- Tutoriels Java Oracle ADF
- Java Basic
- Tutoriels de Java Collections Framework
- Tutoriels Java IO
- Tutoriels Struts2
- Tutoriels Spring Boot
- Tutoriels Spring Cloud
- Tutoriels Maven
- Tutoriels Gradle